Business
Emissions from UK residents and businesses fell by 0.5% in 2024, data shows

Greenhouse gas emissions generated by UK residents and businesses both at home and abroad fell by 0.5% in 2024, provisional figures show.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) said on Friday that the UK’s so-called “residential basis” emissions were 476 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) in 2024.
This was 43.3% below levels in 1990 – the first year the ONS has data for.
Residence basis emissions cover those generated by British residents and businesses regardless of where they occur geographically.
The 0.5% fall from 2023 continues a general downward trend since the data time series began in 1990.
The manufacturing industry was the largest contributor to this total decrease in 2024, falling by 7.4% from 2023, according to the ONS.
Meanwhile, consumer spending remained the largest single contributor to UK emissions on a residence basis, at 26.0% of the 2024 UK total, the figures show.
These emissions were found to have risen by 1.7% in 2024 compared with 2023, marking the first time annual consumer expenditure emissions have increased since 2021, during the coronavirus pandemic.
This rise was largely driven by a 4.1% increase in residential natural gas combustion, the ONS said.
The second largest contributor to the UK’s emissions last year was found to be the transport sector at 16.1%.
It came after emissions from this industry increased by 4.5% in 2024, continuing a general rise for transport since 2021.
The ONS also published figures on changes in UK emissions intensity – which measures environmental efficiency by comparing the quantity of emissions to the economic output.
Between 2023 and 2024, UK emissions intensity fell from 0.16 to 0.15 thousand tonnes of CO2e per million pounds of gross value added (GVA).
Residence basis emissions, which are published by the ONS, can include emissions generated by UK residents overseas, such as travel, and from UK-registered companies operating abroad but they exclude those generated within the UK by foreign residents and businesses.
They differ from the Energy Department’s (Desnz) figures – last released in March – that calculate the emissions generated within the UK’s borders.
In 2024, these territorial emissions were 371.4 million tonnes of carbon equivalent – which was 3.5% lower than 2023 and 54.2% lower than 1990.
Business
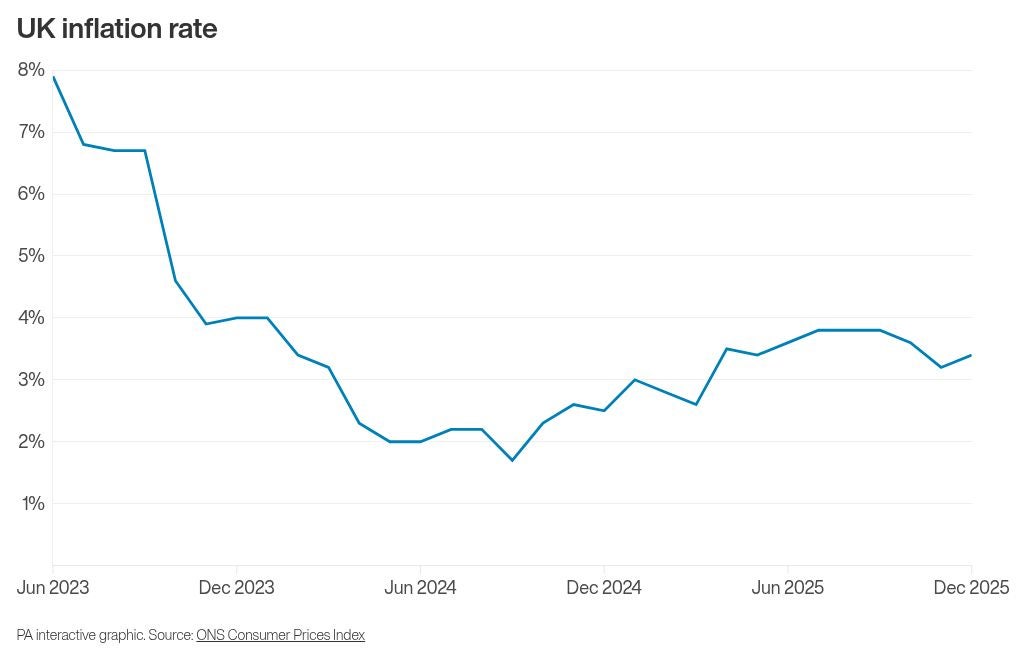
How inflation rebound is set to affect UK interest rates

Interest rates are widely expected to remain at 3.75% as Bank of England policymakers prioritise curbing above-target inflation while also monitoring economic growth, according to expert analysis.
The Bank’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is anticipated to leave borrowing costs unchanged when it announces its latest decision on Thursday, marking its first interest rate setting meeting of the year.
This follows a rate cut delivered before Christmas, which was the fourth such reduction.
At the time, Governor Andrew Bailey noted that the UK had “passed the recent peak in inflation and it has continued to fall”, enabling the MPC to ease borrowing costs. However, he cautioned that any further cuts would be a “closer call”.
Since that decision, official data has revealed that inflation unexpectedly rebounded in December, rising for the first time in five months.
The Consumer Prices Index (CPI) inflation rate reached 3.4% for the month, an increase from 3.2% in November, with factors such as tobacco duties and airfares contributing to the upward pressure on prices.
Economists suggest this inflation uptick is likely to reinforce the MPC’s inclination to keep rates steady this month.
Philip Shaw, an analyst for Investec, stated: “The principal reason to hold off from easing again is that at 3.4% in December, inflation remains well above the 2% target.”
He added: “But with the stance of policy less restrictive than previously, there are greater risks that further easing is unwarranted.”
Shaw also highlighted other data points the MPC would consider, including gross domestic product (GDP), which saw a return to growth of 0.3% in November – a potentially encouraging sign for policymakers.
Matt Swannell, chief economic advisor to the EY ITEM Club, affirmed: “Keeping bank rate unchanged at 3.75% at next week’s meeting looks a near-certainty.”
He noted that while some MPC members who favoured a cut in December still have concerns about persistent wage growth and inflation, recent data has not been compelling enough to prompt back-to-back reductions.
Edward Allenby, senior economic advisor at Oxford Economics, forecasts the next rate cut to occur in April.
He explained: “The MPC will continue to face a delicate balancing act between supporting growth and preventing inflation from becoming entrenched, with forthcoming data on pay settlements likely to play a decisive role in shaping the next policy move.”
The Bank’s policymakers have consistently voiced concerns regarding the pace of wage increases in the UK, which can fuel overall inflation.
Business
Budget 2026: India pushes local industry as global tensions rise

India’s budget focuses on infrastructure and defence spending and tax breaks for data-centre investments.
Source link
Business
New Income Tax Act 2025 to come into effect from April 1, key reliefs announced in Budget 2026

New Delhi: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Sunday said that the Income Tax Act 2025 will come into effect from April 1, 2026, and the I-T forms have been redesigned such that ordinary citizens can comply without difficulty for ease of living.
The new measures include exemption on insurance interest awards, nil deduction certificates for small taxpayers, and extension of the ITR filing deadline for non-audit cases to August 31.
Individuals with ITR 1 and ITR 2 will continue to file I-T returns till July 31.
“In July 2024, I announced a comprehensive review of the Income Tax Act 1961. This was completed in record time, and the Income Tax Act 2025 will come into effect from April 1, 2026. The forms have been redesigned such that ordinary citizens can comply without difficulty, for) ease of living,” she said while presenting the Budget 2026-27
In a move that directly eases cash-flow pressure on individuals making overseas payments, the Union Budget announced lower tax collection at source across key categories.
“I propose to reduce the TCS rate on the sale of overseas tour programme packages from the current 5 per cent and 20 per cent to 2 per cent without any stipulation of amount. I propose to reduce the TCS rate for pursuing education and for medical purposes from 5 per cent to 2 per cent,” said Sitharaman.
She clarified withholding on services, adding that “supply of manpower services is proposed to be specifically brought within the ambit of payment contractors for the purpose of TDS to avoid ambiguity”.
“Thus, TDS on these services will be at the rate of either 1 per cent or 2 per cent only,” she mentioned during her Budget speech.
The Budget also proposes a tax holiday for foreign cloud companies using data centres in India till 2047.
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoPSL 11: Local players’ category renewals unveiled ahead of auction
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoStrap One of Our Favorite Action Cameras to Your Helmet or a Floaty
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoWanted Olympian-turned-fugitive Ryan Wedding in custody, sources say
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoThree dead after suicide blast targets peace committee leader’s home in DI Khan
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThis Mega Snowstorm Will Be a Test for the US Supply Chain
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoStorylines shaping the 2025-26 men’s college basketball season
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoUFC Head Dana White credits Trump for putting UFC ‘on the map’
-

 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days agoClaire Danes reveals how she reacted to pregnancy at 44






