Business
US beef prices are soaring. Will Trump’s plans lower them?

Danielle KayeBusiness reporter
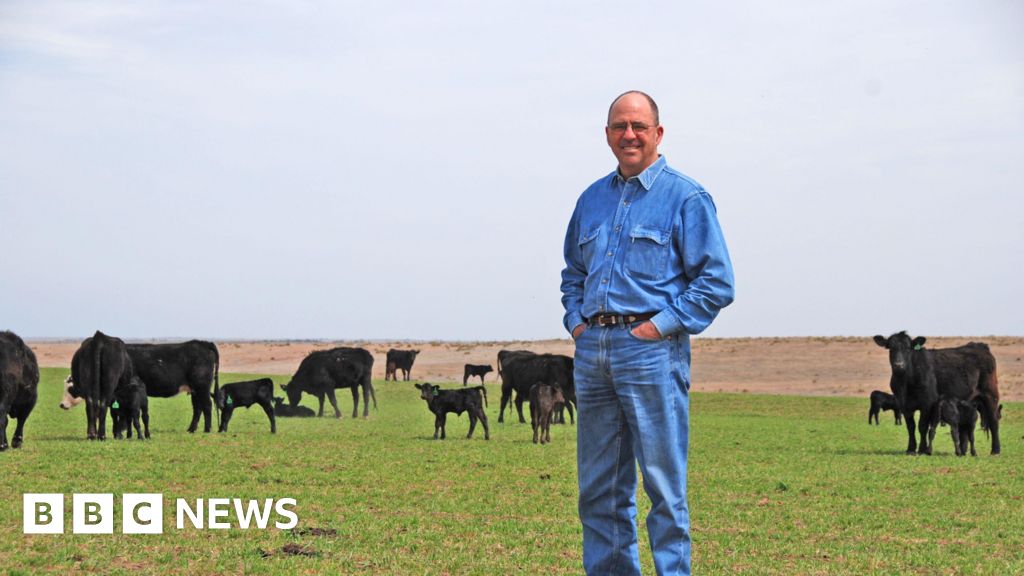
 Mike Callicrate
Mike CallicrateBeef prices have gotten so high in the US that it has become a political problem.
Even US President Donald Trump, who long ago declared inflation “dead”, is talking about it, as the issue threatens to undercut his promises to bring down grocery prices for Americans.
This week, he took to social media, urging ranchers to lower prices for their cattle.
But his demand – and other proposals his administration has floated to address the issue – has sparked a backlash among ranchers, who worry some of his solutions will make it harder for them to make a living, while making little dent at the grocery store.
The number of beef cattle farmers and ranchers in the US has dwindled steadily since 1980, reducing domestic supplies and driving up prices, as demand remains high.
The country’s cattle inventory has fallen to its lowest level in nearly 75 years, while the US has lost more than 150,000 cattle ranches since 2017 – a 17% drop, according to the Agriculture Department.
Ranchers say they are under pressure from four decades of consolidation among the meat processors that buy their livestock, while high costs for key inputs like fertiliser and equipment have intensified the strain.
The contraction in the industry has worsened as several years of drought have forced ranchers to slash their herd sizes.
Christian Lovell, a cattle rancher in Illinois, says parts of his farm that were lush and grassy when he was a child have now dried up, limiting where his cows can graze.
“You put all these together and you have a recipe for a really broken market,” says Mr Lovell, who works with advocacy group Farm Action.
Beef inflation
Retail prices for beef mince rose 12.9% in the 12 months to September, and beef steaks were up 16.6%, according to US inflation data published on Friday by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
A pound of ground chuck – richer mince from the neck and shoulder of cows – now costs an average of $6.33 (£4.75), compared to $5.58 a year ago.
The increases have significantly outpaced general food inflation, which stood at 3.1%.
“The cattle herd has been getting smaller for the last several years, yet people are still wanting that American beef – hence the high prices,” says Brenda Boetel, a professor of agricultural economics at the University of Wisconsin, River Falls.
Derrell Peel, a professor of agricultural economics at Oklahoma State University, says he expected prices to remain elevated until at least the end of the decade, noting that it takes years to replenish herds.
The Trump administration’s “hands are tied” when it comes to interventions that will help lower prices, he adds.
 Reuters
Reuters‘Chaos’ for US producers
The Agriculture Department unveiled what it called a “big package” this week aimed at ramping up domestic beef production by opening more land for cattle grazing and supporting small meat processors.
That proposal came after Trump drew the ire of ranchers when he proposed importing more beef from Argentina, potentially quadrupling US purchases.
Eight House Republicans responded with a letter expressing concerns about the plans.
Even the National Cattlemen’s Beef Association, which has voiced support for Trump’s policies in the past, said the import plan “only creates chaos at a critical time of the year for American cattle producers, while doing nothing to lower grocery store prices”.
Trump responded by assuring farmers that he was helping them in other ways, noting that tariffs that were limiting imports from Brazil.
“It would be nice if they would understand that, but they also have to get their prices down, because the consumer is a very big factor in my thinking, also,” Trump wrote.
But that has failed to quell the furore.
Justin Tupper, president of the US Cattlemen’s Association, says only the big four meat packers would benefit from Trump’s import plan in his view.
“I don’t see that lowering prices here at all,” he says.
‘These are consolidated markets’
Some say the US government could make an impact if it focused on the way a handful of companies dominate the market for meat processing.
Today, just four firms control more than 80% of the beef slaughtering and packing market.
“These are consolidated markets gouging ranchers and gouging consumers at the store,” said Austin Frerick, an agricultural and antitrust policy expert and a fellow at Yale University.
The meat processing firms – Tyson, JBS, Cargill and National Beef – have faced several lawsuits, including one filed by McDonald’s alleging that they colluded to inflate the price of beef.
Though Trump revoked a Biden-era order earlier this year directing agencies to tackle corporate consolidation across the food supply chain, his administration has taken other steps to investigate competition issues in the agricultural industry.
‘We’re not going to rebuild this cow herd’
Mike Callicrate runs a cattle ranch in St Francis, Kansas. He says the only way he has managed to stay in the industry was by cutting out the middleman and setting up his own stores to reach consumers directly.
But he acknowledged that most ranchers do not have the money to make that shift. Many have left the industry – and see no incentive to jump back in.
“We’re not going to rebuild this cow herd – not until we address market concentration,” Mr Callicrate says.
He adds that he supported the Agriculture Department’s plans to open up more cattle grazing land.
“But unless we have a market”, anyone would be a “fool to get into the cattle business”, he says.
 Bill Bullard
Bill BullardBill Bullard found himself in the first wave of ranchers pushed out as the meat processing industry started to consolidate in the early 1980s.
He closed down his 300-cow operation in South Dakota in 1985.
Now the chief executive of R-CALF USA, a cattle producer trade association, he says it was only in the last year or so that ranchers had received good prices for their livestock, as supply dropped to such a low level that the prices paid by meat processors “simply had to increase”.
Still, reliance on imports and meat packers’ buying power persists, Mr Bullard says, meaning ranchers “lack confidence in the integrity of the marketplace” and remain reluctant to grow their herds.
He says he does not have confidence that the president’s ideas would fix the issues.
“He’s focused on the symptoms and not the problems.”
Business
How inflation rebound is set to affect UK interest rates

Interest rates are widely expected to remain at 3.75% as Bank of England policymakers prioritise curbing above-target inflation while also monitoring economic growth, according to expert analysis.
The Bank’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is anticipated to leave borrowing costs unchanged when it announces its latest decision on Thursday, marking its first interest rate setting meeting of the year.
This follows a rate cut delivered before Christmas, which was the fourth such reduction.
At the time, Governor Andrew Bailey noted that the UK had “passed the recent peak in inflation and it has continued to fall”, enabling the MPC to ease borrowing costs. However, he cautioned that any further cuts would be a “closer call”.
Since that decision, official data has revealed that inflation unexpectedly rebounded in December, rising for the first time in five months.
The Consumer Prices Index (CPI) inflation rate reached 3.4% for the month, an increase from 3.2% in November, with factors such as tobacco duties and airfares contributing to the upward pressure on prices.
Economists suggest this inflation uptick is likely to reinforce the MPC’s inclination to keep rates steady this month.
Philip Shaw, an analyst for Investec, stated: “The principal reason to hold off from easing again is that at 3.4% in December, inflation remains well above the 2% target.”
He added: “But with the stance of policy less restrictive than previously, there are greater risks that further easing is unwarranted.”
Shaw also highlighted other data points the MPC would consider, including gross domestic product (GDP), which saw a return to growth of 0.3% in November – a potentially encouraging sign for policymakers.
Matt Swannell, chief economic advisor to the EY ITEM Club, affirmed: “Keeping bank rate unchanged at 3.75% at next week’s meeting looks a near-certainty.”
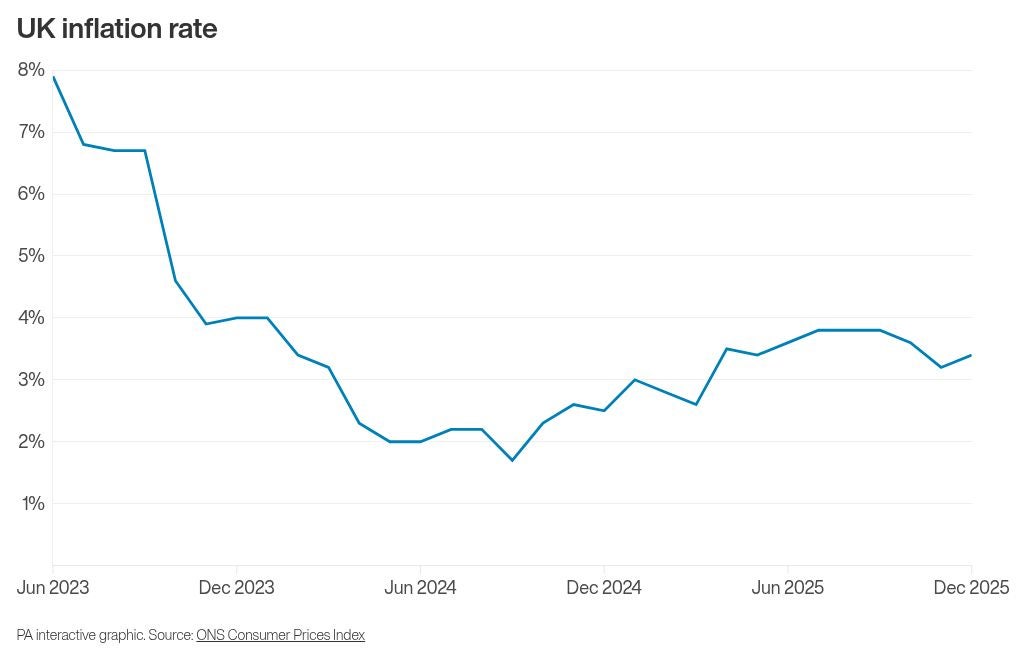
He noted that while some MPC members who favoured a cut in December still have concerns about persistent wage growth and inflation, recent data has not been compelling enough to prompt back-to-back reductions.
Edward Allenby, senior economic advisor at Oxford Economics, forecasts the next rate cut to occur in April.
He explained: “The MPC will continue to face a delicate balancing act between supporting growth and preventing inflation from becoming entrenched, with forthcoming data on pay settlements likely to play a decisive role in shaping the next policy move.”
The Bank’s policymakers have consistently voiced concerns regarding the pace of wage increases in the UK, which can fuel overall inflation.
Business
Budget 2026: India pushes local industry as global tensions rise

India’s budget focuses on infrastructure and defence spending and tax breaks for data-centre investments.
Source link
Business
New Income Tax Act 2025 to come into effect from April 1, key reliefs announced in Budget 2026

New Delhi: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Sunday said that the Income Tax Act 2025 will come into effect from April 1, 2026, and the I-T forms have been redesigned such that ordinary citizens can comply without difficulty for ease of living.
The new measures include exemption on insurance interest awards, nil deduction certificates for small taxpayers, and extension of the ITR filing deadline for non-audit cases to August 31.
Individuals with ITR 1 and ITR 2 will continue to file I-T returns till July 31.
“In July 2024, I announced a comprehensive review of the Income Tax Act 1961. This was completed in record time, and the Income Tax Act 2025 will come into effect from April 1, 2026. The forms have been redesigned such that ordinary citizens can comply without difficulty, for) ease of living,” she said while presenting the Budget 2026-27
In a move that directly eases cash-flow pressure on individuals making overseas payments, the Union Budget announced lower tax collection at source across key categories.
“I propose to reduce the TCS rate on the sale of overseas tour programme packages from the current 5 per cent and 20 per cent to 2 per cent without any stipulation of amount. I propose to reduce the TCS rate for pursuing education and for medical purposes from 5 per cent to 2 per cent,” said Sitharaman.
She clarified withholding on services, adding that “supply of manpower services is proposed to be specifically brought within the ambit of payment contractors for the purpose of TDS to avoid ambiguity”.
“Thus, TDS on these services will be at the rate of either 1 per cent or 2 per cent only,” she mentioned during her Budget speech.
The Budget also proposes a tax holiday for foreign cloud companies using data centres in India till 2047.
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoPSL 11: Local players’ category renewals unveiled ahead of auction
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoStrap One of Our Favorite Action Cameras to Your Helmet or a Floaty
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoWanted Olympian-turned-fugitive Ryan Wedding in custody, sources say
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoThree dead after suicide blast targets peace committee leader’s home in DI Khan
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThis Mega Snowstorm Will Be a Test for the US Supply Chain
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoStorylines shaping the 2025-26 men’s college basketball season
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoUFC Head Dana White credits Trump for putting UFC ‘on the map’
-

 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days agoClaire Danes reveals how she reacted to pregnancy at 44







