Business
Isas, cars and pensions – how the Budget affects you?

Kevin PeacheyCost of living correspondent
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesChancellor Rachel Reeves is announcing her Budget, but details were published early by the official forecaster.
Here are the key measures and how they will affect you and your money.
You may pay more tax
The amount of income at which you pay different rates of income tax will still not be increased in line with rising prices.
Instead the bands – known as tax thresholds – will stay frozen until 2031. That is three years longer than previously planned.
This means any kind of pay rise could drag you into a higher tax bracket, or see a greater proportion of your income taxed than would otherwise be expected.
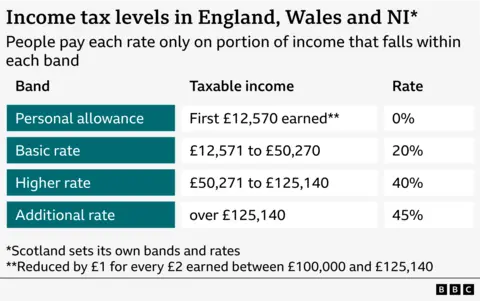
Scotland has its own income tax rates.
You may not earn enough to pay income tax, so VAT, paid when buying goods and services, may hit you harder and that’s been left unchanged.
Driving an electric car will be more expensive
Electric vehicle and hybrid car drivers will be taxed for using the road from 2028.
EV drivers will be charged per mile, on top of other road taxes, in new road pricing.
Calculating the number of miles that drivers cover is difficult.
But fuel duty will continue to be frozen.
You will get a rise if you’re on low pay
The chancellor confirmed increases in April for those on minimum wages.
It means:
- Eligible workers aged 21 and over on the National Living Wage will receive £12.71 an hour, up from £12.21
- If you are aged 18, 19 or 20, the National Minimum Wage increase to £10.85 an hour, up from £10
- For those aged 16 or 17, the minimum wage will rise to £8 an hour, up from £7.55
The separate apprentice rate which applies to eligible people under 19 – or those over 19 in the first year of an apprenticeship – will also increase to £8 an hour, from £7.55.
If your home is worth £2m you will pay more tax
Anyone who lives in a home valued at £2m or more in England will face a council tax surcharge from April 2028.
There will be four price bands with the surcharge rising from £2,500 for a property valued in the £2m to £2.5m band, to £7,500 for a property valued in the highest band of £5m or more
While known as a mansion tax, it may also capture homes in expensive areas, and will be levied on about 100,000 properties, primarily in London and south east England.
The move will require the valuation of homes in the top council tax bands – F, G and H – for the first time since 1991.
You can check your council tax band here if you are in England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland.
Travelling by train in England won’t cost you more
Regulated rail fares in England will be frozen until March 2027 – the first time they have been left unchanged for 30 years.
These fares include season tickets covering most commuter routes, some off-peak return tickets on long-distance journeys and flexible tickets for travel in and around major cities.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesThe freeze only relates to travel in England, and also only applies to services run by England-based train operating companies.
Train operators are free to set prices for unregulated fares.
The bus fare cap of £3 for a single journey, covering most bus journeys in England, is already in place until March 2027.
Saving in a cash Isa will be restricted
The amount of money that can be saved tax-free each year in a cash Isa (Individual Savings Account) will be reduced from £20,000 to £12,000 a year for the under 65s.
Ministers want people to invest more, which comes with greater risk but could help boost growth – a key objective for the government.
There are questions over whether people would naturally put their money into stocks and shares Isas as a result of the less generous tax break on cash Isas.
About a quarter of those who save money into a cash Isa currently save more than £12,000 a year.
But many of those are pensioners, and the chancellor said the over-65s will still be able to save up to £20,000 in cash.
Separately, the Help to Save scheme, which helps those on low incomes and on universal credit to put money aside, will be extended from 2028.
If you have three children you may get more money
At present, parents can only claim universal credit or tax credits for their first two children.
The chancellor says this two-child cap will be scrapped in April next year.
A limit on what you can save into a pension through salary sacrifice
A third of private sector employees and a tenth of public sector workers use a salary sacrifice scheme for their pension savings.
These workers give up a portion of their salary in return for their employer paying the equivalent amount into their pension. The benefit to both employee and employee is that they make savings in national insurance.
A £2,000-a-year cap on the amount that can be put into pensions through this salary sacrifice arrangement will be in place from April 2029.
Employees would still get income tax relief on their pension contributions, but some argue the move will reduce pension saving incentives.
Most benefits and the state pension will rise
Some benefits, including all the main disability benefits, such as personal independence payment, attendance allowance and disability living allowance, as well as carer’s allowance will rise by 3.8% in April, in line with rising prices.
There will be a string of changes to universal credit in April, following announcements made earlier by the government.
The state pension in April will rise by 4.8% in line with average wages, which means:
- the new flat-rate state pension – for those who reached state pension age after April 2016 – will increase to £241.30 a week, or £12,547.60 a year, a rise of £574.60
- the old basic state pension – for those who reached state pension age before April 2016 – will go up to £184.90 a week, or £9,614.80 a year, a rise of £439.40
In general, you need 35 years of qualifying contributions to get a full state pension.
This brings the state pension closer to being subject to income tax – a source of some debate. It will also reignite discussions over the “fairness” of the so-called triple lock.
More on the milkshake tax, prescription charges and Motability
A range of other measures in the Budget had already become clear or been announced in recent days. They included:
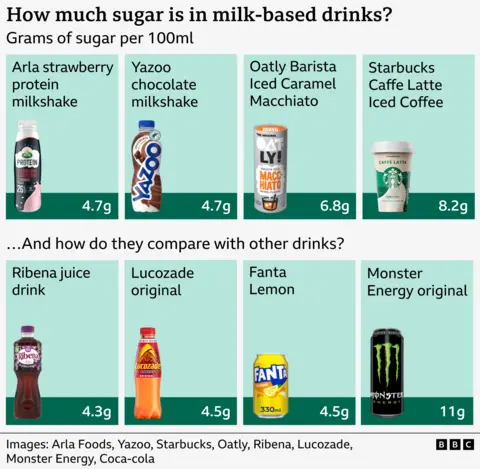
- The UK tax on fizzy drinks will be extended to milk-based products in 2028, taking in pre-packaged milkshakes and coffees that are high in sugar. This may push up prices, or lead to ingredient changes
- The cost of a single NHS prescription in England will be frozen at £9.90 for the second year in a row in April
- Disabled people who have a car through the Motability scheme will no longer be allowed “premium” vehicles such as BMWs, Mercedes, Audi, Alfa Romeo and Lexus
- England’s mayors could be given the powers to charge a levy on overnight stays, sometimes referred to as a ‘tourist tax’. Mayors would decide the level of the charge, and how to spend the money in their areas, under the plans which will be consulted upon
Business
Govt keeps petrol, diesel prices unchanged for coming fortnight – SUCH TV

The government on Thursday kept petrol and high-speed diesel (HSD) prices unchanged at Rs253.17 per litre and Rs257.08 per litre respectively, for the coming fortnight, starting from January 16.
This decision was notified in a press release issued by the Petroleum Division.
Earlier, it was expected that the prices of all petroleum products would go down by up to Rs4.50 per litre (over 1pc each) today in view of variation in the international market.
Petrol is primarily used in private transport, small vehicles, rickshaws, and two-wheelers, and directly impacts the budgets of the middle and lower-middle classes.
Meanwhile, most of the transport sector runs on HSD. Its price is considered inflationary, as it is mostly used in heavy transport vehicles, trains, and agricultural engines such as trucks, buses, tractors, tube wells, and threshers, and particularly adds to the prices of vegetables and other eatables.
The government is currently charging about Rs100 per litre on petrol and about Rs97 per litre on diesel.
Business
Serial rail fare evader faces jail over 112 unpaid tickets

One of Britain’s most prolific rail fare dodgers could face jail after admitting dozens of travel offences.
Charles Brohiri, 29, pleaded guilty to travelling without buying a ticket a total of 112 times over a two-year period, Westminster Magistrates’ Court heard.
He could be ordered to pay more than £18,000 in unpaid fares and legal costs, the court was told.
He will be sentenced next month.
District Judge Nina Tempia warned Brohiri “could face a custodial sentence because of the number of offences he has committed”.
He pleaded guilty to 76 offences on Thursday.
It came after he was convicted in his absence of 36 charges at a previous hearing.
During Thursday’s hearing, Judge Tempia dismissed a bid by Brohiri’s lawyers to have the 36 convictions overturned.
They had argued the prosecutions were unlawful because they had not been brought by a qualified legal professional.
But Judge Tempia rejected the argument, saying there had been “no abuse of this court’s process”.
Business
JSW Likely To Launch Jetour T2 SUV In India This Year: Reports

JSW Jetour T2 Launch: JSW Motors Limited, the passenger vehicle arm of the JSW Group, is reportedly preparing to enter the Indian car market this year. It has partnered with Jetour, a China-based automotive brand owned by Chery Automobile, and the Jetour T2 SUV could be the company’s first product, according to the reports.
Media reports suggest that the launch will happen independently and not under the JSW MG Motor India joint venture. The SUV will wear a JSW badge and name, instead of the Jetour branding. The upcoming SUV will be assembled at JSW’s upcoming greenfield manufacturing facility in Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, Maharashtra.
According to the reports, the company plans to have the vehicle on sale by the third quarter of this year. With this move, JSW aims to establish itself as a standalone carmaker in India.
Expected Powertrain
The SUV is likely to arrive with a 1.5-litre plug-in hybrid setup. Internationally, this hybrid powertrain is offered with both front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive options. It is still unclear which version will be introduced in India.
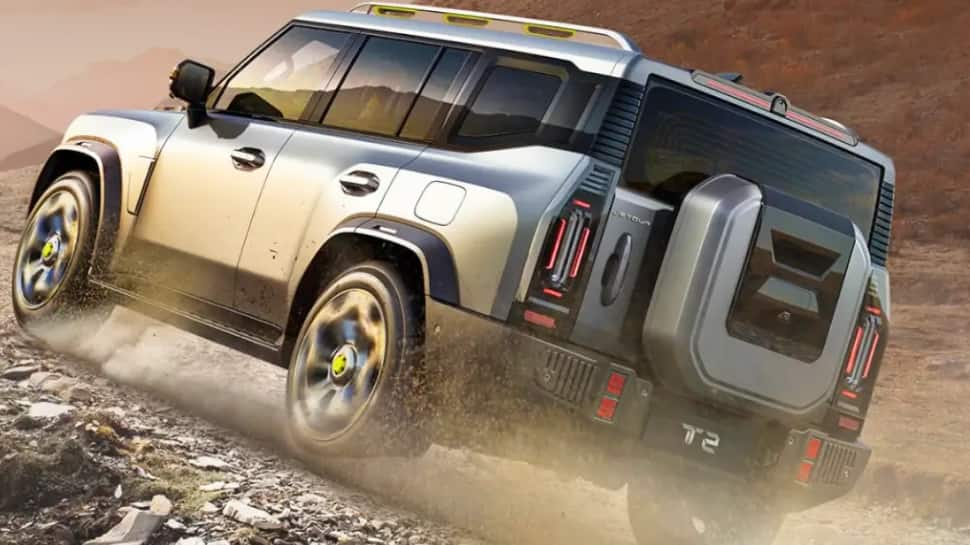
Design
In terms of design, the T2 is a large and rugged-looking SUV. It has a boxy and upright stance, similar to vehicles like the Land Rover Defender. Despite its tough appearance, it uses a monocoque chassis instead of a ladder-frame construction.
Size
The SUV measures around 4.7 metres in length and nearly 2 metres in width. This makes it larger than the Tata Safari, even though it is a five-seater. A longer 7-seat version is also sold in some markets.
Price
Pricing details for India are yet to be announced. For reference, the front-wheel-drive five-seat T2 i-DM is priced at AED 1,44,000 (around Rs 35 lakh) in the UAE.
Jetour
Jetour is a brand owned by Chinese automaker Chery. Launched in 2018, it focuses mainly on SUVs and is present in markets across China, the Middle East, Africa, Southeast Asia and Latin America.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoUK says provided assistance in US-led tanker seizure
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoDoes new US food pyramid put too much steak on your plate?
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoWhy did Nick Reiner’s lawyer Alan Jackson withdraw from case?
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoTrump moves to ban home purchases by institutional investors
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoClock is ticking for Frank at Spurs, with dwindling evidence he deserves extra time
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoPGA of America CEO steps down after one year to take care of mother and mother-in-law
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoBulls dominate as KSE-100 breaks past 186,000 mark – SUCH TV
-
Sports6 days ago
Commanders go young, promote David Blough to be offensive coordinator







