Business
Planning To Sell Family Heirloom Gold? Check Tax Rules To Avoid Hassles

Last Updated:
Selling inherited gold? You might owe capital gains tax. Here’s what Indian tax law says about jewellery passed down from parents or grandparents.

According to Indian tax laws, inherited gold is considered a capital asset, so any profit made from selling it may be subject to capital gains tax. (AI Generated)
Gold has long been a symbol of tradition, prosperity, and financial security for Indian families. Often passed down through generations, gold jewellery is typically received as part of family heritage, gifted during weddings or other significant occasions by parents and grandparents.
However, if the time has come to sell this inherited gold, it’s important to understand how taxation applies.
Is Inherited Gold Taxable? Yes, Here’s How
According to Indian tax laws, inherited gold is treated as a capital asset. This means that if you sell it, capital gains tax may apply on the profit made.
A unique aspect of inherited gold is that, for tax purposes, the purchase date and cost are considered the same as those of the original owner, such as your mother or grandmother.
For instance, if your grandmother purchased the gold in 1981 and you received it during your marriage, the cost and purchase date from 1981 are used for calculating capital gains.
Gold Purchased Before 2001? You Have An Advantage
If the gold was originally purchased before April 1, 2001, you have the option to use the Fair Market Value (FMV) as of April 1, 2001 instead of the actual purchase price. This often benefits the seller, especially when historical records are missing or unclear.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Capital Gains: What’s The Difference?
It’s essential to understand the distinction between short-term and long-term capital gains, as the tax treatment differs:
Previously, gold held for more than 36 months was considered a long-term asset. After the Finance Act 2024, this threshold has been reduced to 24 months.
So now, if you’ve held the gold for over 24 months, the profit is treated as a long-term capital gain, and you’ll be taxed at 12.5% (without indexation). However, if you sell the gold within 24 months, the profit is considered a short-term gain, and will be taxed according to your income tax slab.
Gold vs Nifty50 vs Fixed Deposits: Who Wins Over 10 Years?
When comparing returns on various investments over a decade, such as gold, Nifty50, and fixed deposits (FDs), gold has often delivered competitive, if not superior, returns, especially when held for decades. For example, a Rs 1 lakh investment made decades ago in gold could well have outperformed traditional savings instruments.
In cases where the gold is several decades old, the 12.5% long-term capital gains tax will apply, but that still leaves a significant profit margin.
No Purchase Records? Here’s What You Can Do
If you don’t have access to the original purchase records for the inherited gold, don’t worry. You can rely on either:
- A valuation report from a certified jeweller, or
- The historical gold rates published by the local Jewellers’ Association.
These can serve as valid documentation for determining the cost of acquisition during tax assessment.
In conclusion, yes, tax is applicable when selling inherited gold. But the good news is that the rates are reasonable, especially for long-term holdings. With the right paperwork, such as FMV documents or jewellers’ valuation, calculating and filing taxes becomes a straightforward task.
So, if you’re planning to sell inherited gold, be informed and prepared, and you can make the most of your family treasure, both sentimentally and financially.
Read More
Business
Two ships hit near Strait of Hormuz as fears grow of oil price rises

International shipping is said to have come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with fears of disruption already pushing up global oil prices.
Source link
Business
Khamenei dead, Middle East on edge: What will be the implications of Trump’s ‘Epic fury’ on stock markets, gold & oil? – The Times of India

The global markets are in for a phase of enhanced turmoil and uncertainty! The ongoing tensions in the Middle East after US and Israel’s strikes on Iran and Ali Khamenei’s death may have investors running for cover – looking for an asset class that is safer.During the night of February 27–28, the United States and Israel carried out joint aerial strikes on Iran as part of “Operation Epic Fury.” Statements by President Trump openly referring to regime change suggest that the confrontation could evolve into a prolonged campaign rather than remain a limited exchange, say market analysts at Franklin Templeton Institute.What does the situation mean for stock markets, energy markets (oil), gold and other asset classes? Here’s what Franklin Templeton Institute analysts have to say:From a market perspective, the key uncertainty is whether the conflict remains confined to direct military engagement or expands into disruptions affecting energy supplies and logistics networks, which would sustain a higher and more persistent risk premium.At the centre of the ongoing uncertainty from a global market and trade perspective is the Strait of Hormuz. While a complete blockade would carry severe consequences for Iran itself, the country has the capability to disrupt maritime traffic through tactics such as vessel harassment, seizures, drone activity, cyber operations, or the use of proxy forces.
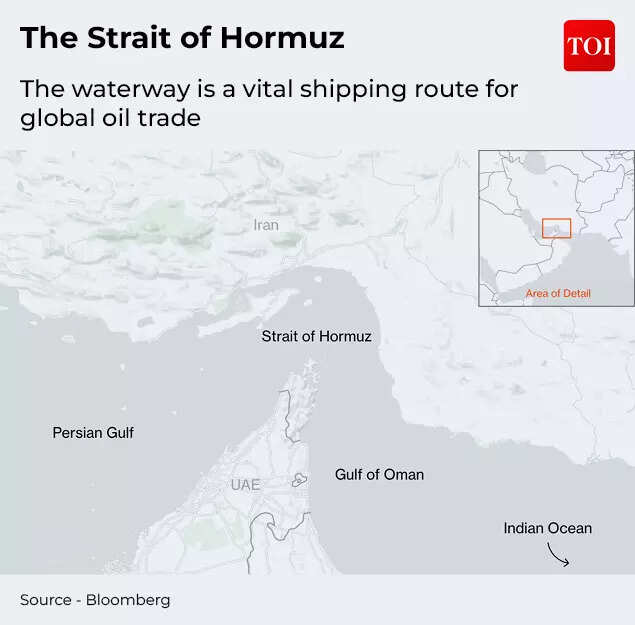
Strait of Hormuz
The most immediate economic impact is expected in energy markets, where crude oil and natural gas prices are likely to move higher, they say. Such actions, feel analysts, will keep geopolitical risk premiums at high levels. In 2024, approximately 20 million barrels per day moved through the Strait of Hormuz, which is around one-fifth of global petroleum liquids consumption. Even a limited interference – which can be caused by delays, rerouting, or isolated seizure – can push prices higher through increased risk perception well before any actual shortages emerge.Liquefied natural gas should not be overlooked in this context. Qatar has the world’s third-largest LNG export capacity, and roughly one-fifth of global LNG shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, largely consisting of Qatari exports. As a result, shipping risks in the region affect gas markets as significantly as oil markets.Also Read | US-Israel strikes on Iran: How will India be hit by Strait of Hormuz closure? ExplainedShipping expenses have already begun to rise, with insurance costs acting as a major driver. Insurers have started issuing cancellation notices and revising war-risk premiums for voyages in the Gulf region. Some routes have reportedly seen premium increases of up to about 50%, while earlier periods of tension recorded rises exceeding 60% on important trade corridors. These developments effectively tighten supply conditions even when production levels remain unchanged.The possibility of the conflict spreading across the region is increasing. Franklin Templeton Institute analysts are of the view that across global financial markets, the immediate response to such shocks is usually driven by adjustments in risk perception rather than by underlying economic changes. “The initial market reaction for this type of event would typically see Treasury yields move lower and equities lower—mostly a risk-premium repricing. Impacts on activity/earnings may be delayed and uneven. The US dollar reaction is not guaranteed; gold tends to benefit while bitcoin has been trading like a risk asset (i.e., down with equities), reinforcing that it’s not typically a reliable hedge/diversifier in geopolitical drawdowns,” say Franklin Templeton Institute analysts.However, they note that experience shows markets often come to view geopolitical disruptions as temporary. Initial spikes in risk premiums are frequently followed by the realization that the overall effect on corporate profitability is limited. The duration of the conflict, developments in shipping and insurance costs, and the eventual resolution will be more important than the initial headlines.“We would not yet label this a clean buy-the-dip setup—duration, shipping/insurance mechanics, and the endgame matter more than the first headline,” they say.From an investment perspective, the near-term outlook favours sectors linked to energy markets, as well as companies benefiting from higher shipping and insurance costs, along with defence-related industries, the analysts say. At the same time, caution is warranted toward emerging markets that depend heavily on energy imports and toward cyclical sectors sensitive to fuel and logistics costs, including airlines and certain industrial segments.“For protection, we prefer oil upside/volatility structures and selective gold exposure over broad equity shorts—the path will be driven more by shipping/insurance reality than by the new cycle,” they conclude.
Business
Crude oil prices in focus: OPEC+ increases output by 206,000 bpd amid Middle East tensions – The Times of India

OPEC+ on Sunday announced a higher-than-expected increase in oil production quotas, days after US and Israeli strikes on Tehran triggered Iranian retaliation across the Middle East, according to AFP.The oil producers’ group, which includes Saudi Arabia, Russia and several Gulf states affected by the escalation, said it had “agreed on a production adjustment of 206 thousand barrels per day”.“This adjustment will be implemented in April,” OPEC+ said in a statement.While the cartel did not directly refer to the Iran conflict, it cited “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals” as the rationale behind the output increase.The move comes amid heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, a region critical to global crude oil supply.
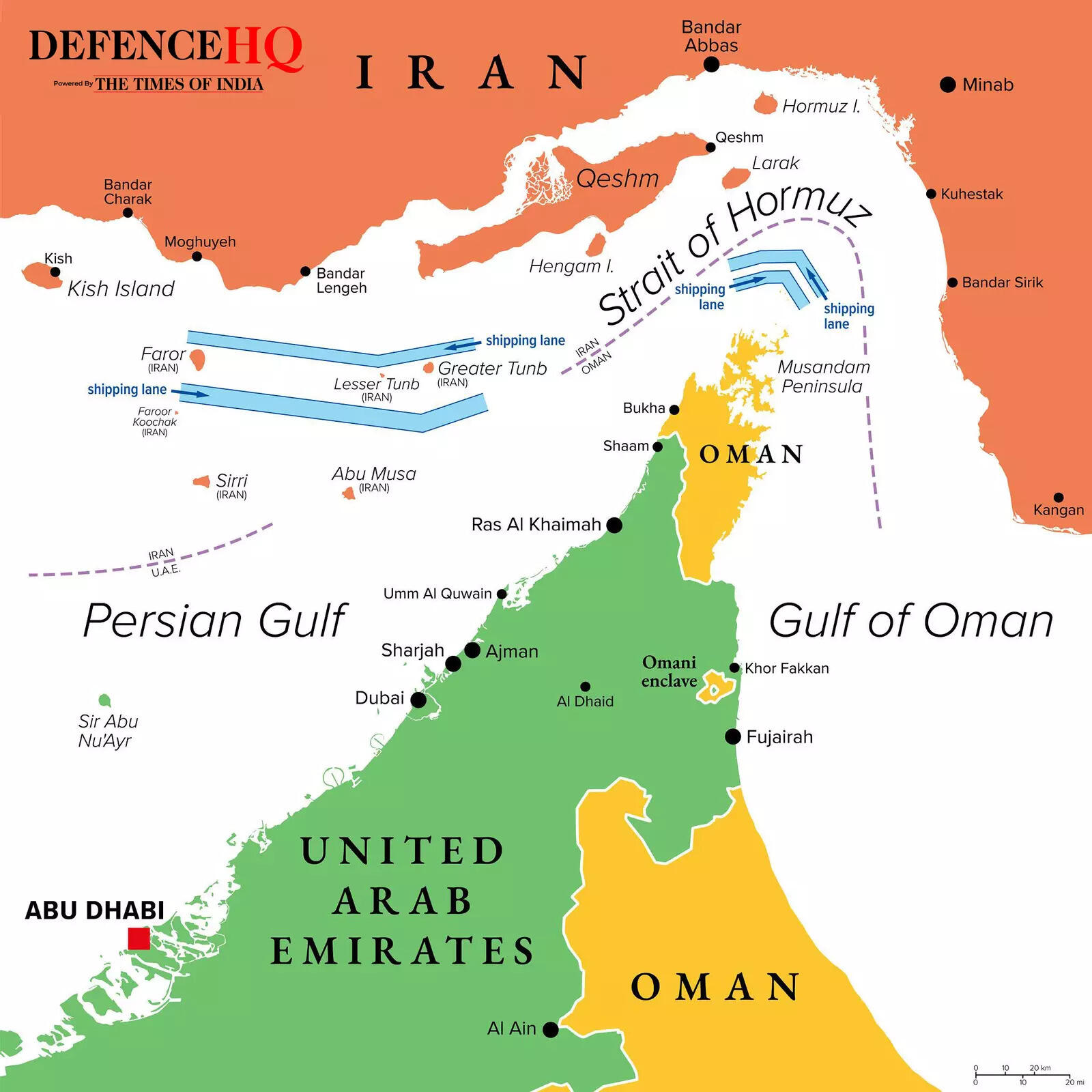
The announcement did not directly reference the outbreak of the Iran conflict, instead attributing the decision to “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals”.Before the meeting, analysts had projected a more modest increase of 137,000 barrels per day.However, Jorge Leon, an analyst at Rystad Energy, cautioned that the agreed hike may not be sufficient to offset the potential impact of escalating tensions on crude oil markets.Leon highlighted the risk of disruption in the Strait of Hormuz, a critical waterway through which nearly a quarter of the world’s seaborne oil supplies transit.Iran’s Revolutionary Guards have reportedly contacted vessels to declare the strait closed. Iranian state television on Sunday said an oil tanker attempting to “illegally” pass through the strait was struck and was sinking, broadcasting footage of a burning tanker at sea.“If oil cannot move through Hormuz, an extra 206,000 barrels per day does very little to ease the market,” Leon said, adding that “logistics and transit risk matter more than production targets right now”.He said the OPEC+ move “is unlikely to calm markets”, noting that “prices will respond to developments in the Gulf and the status of shipping flows, not to a relatively small increase in output.”Apart from Russia and Saudi Arabia, the V8 group includes Kuwait, Oman, Iraq and the United Arab Emirates — all of which were targeted by Iranian attacks for a second consecutive day on Sunday. Algeria and Kazakhstan are also part of the group.
-

 Fashion1 week ago
Fashion1 week agoICE cotton ticks higher on crude oil rally
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoViral monkey Punch makes IKEA toy global sensation: Here’s what it costs
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoSaturday Sessions: Say She She performs "Under the Sun"
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEquinox chairman says ‘health is the new luxury’ as wellness spending soars
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoHow James Milner broke Premier League’s appearances record





