Business
Cava, Chipotle and other fast-casual restaurant chains are finally hit by consumer slowdown

Cava stock tumbled 16% in afternoon trading on Wednesday, making it the latest fast-casual chain to feel Wall Street’s wrath after reporting disappointing quarterly sales.
A year ago, eateries like Chipotle Mexican Grill and Cava were reporting double-digit same-store sales growth, even as the broader restaurant industry posted falling traffic and slumping sales. But times have changed. This spring, fast-casual chains saw foot traffic decline as sales slowed down or even shrank.
To explain the downturn, executives have said that diners are “cautious,” in the words of Sweetgreen CEO Jonathan Neman, or dealing with an economic “fog,” according to Cava CFO Tricia Tolivar.
And just as diners are finding reasons why to cut back on their Shake Shack burgers or Chipotle bowls, investors are trimming their fast-casual holdings after rewarding the companies last year for outperforming the rest of the industry. So far in 2025, Shake Shack shares have fallen 16%; Chipotle stock has slid 28%; Cava shares have tumbled 37%; and Sweetgreen stock has plunged 70%. Of the notable publicly traded fast-casual chains, only Wingstop has managed to stay in the green this year, with gains of 20%.
More broadly, investors have grown more cautious about betting on any restaurants, given weak traffic trends and concerns about consumer spending, according to a research note on Sunday from UBS. Even fast-food companies have struggled with the traffic declines and sluggish sales growth, despite their historical reputation as a safer bet during economic uncertainty.
While some fast-casual chains flagged company-specific reasons for their weaker-than-expected results, executives also said that economic uncertainty is weighing on consumers – and hurting their sales.
Generally, fast-casual diners are higher income and more likely to have white-collar jobs. However, Chipotle CEO Scott Boatwright blamed a pullback from low-income consumers for the chain’s same-store sales declines of 4% in the second quarter.
“You have to look no further than what’s going with our competitors with snack occasions or $5 meals. That’s where the consumer is drifting towards, [with] value as a price point, because of low consumer sentiment. I think as sentiment improves, the business will improve. I think that’s probably the biggest headwind we face,” he told analysts on the company’s earnings conference call on June 23.
The University of Michigan’s index of consumer sentiment slid in April to 52.2, one of its lowest-ever recorded readings. It held at that level in May before rising in June to 60.7.
Fast-casual chains are seeing consumers’ economic anxieties in their own research, too.
“Through our regular consumer research, we hear concerns about elevated prices, future job prospects and general anxiety about the future,” Wingstop CEO Michael Skipworth said on the company’s earnings conference call in late July.
The chicken wing chain reported same-store sales declines of 1.9% for the quarter, a dramatic reversal compared to its growth of 28.7% in the year-ago period.
On the company’s earnings conference call on Thursday, Sweetgreen’s Neman said that the chain saw “a more cautious consumer environment starting in April” — coinciding with the drop in consumer sentiment. A “subdued industry backdrop,” particularly in several of the chain’s biggest urban markets, contributed to Sweetgreen’s “really, really rough quarter,” according to Neman.
That’s one reason why the salad chain reported a steeper-than-expected decline in its same-store sales and cut its full-year forecast for the second straight quarter. Sweetgreen executives also attributed the weak quarterly performance to a tough comparison to last year’s steak launch and the transition of its loyalty program.
To improve its value perception among customers, Sweetgreen is increasing its chicken and tofu portions by 25%, improving its chicken and salmon recipes and implementing some promotional pricing, like $13 menu bowl drops for its loyalty program members.
As for Cava, the company had been wowing investors with impressive same-store sales growth since its initial public offering two years ago. But this quarter, the Mediterranean chain reported same-store sales growth of 2.1%, well below Wall Street projections of 6.1%. Executives said that it faced difficult comparisons to the year-ago period’s same-store sales growth of 14.4%, which was fueled by its own steak launch and strong demand at newer restaurant locations that waned this year.
“Cava isn’t so special after all. After blowing out same store sales in Q1 of 10.8%, it fell in line with the industry at 2.1% in Q2. It’s not negative, so that’s helpful,” Tracey Ryniec, stock strategist at Zacks Investment Research, said.
Cava executives also acknowledged that economic concerns are weighing on diners.
“Certainly, we’re operating in a fluid macroeconomic environment and it’s one that sort of creates a fog for consumers where things are changing constantly and it’s hard to see the clear. And during those times, they tend to step off of the gas,” Tolivar said on the company’s conference call on Tuesday evening.
Still, Cava isn’t seeing consumers trade down to cheaper protein options, or experiencing any other deeper business concerns, co-founder and CEO Brett Schulman said. And as it enters the third quarter, its same-store sales have improved, Tolivar said.
And Cava isn’t the only fast-casual eatery anticipating a return to form in the latter half of the year, especially as consumer sentiment improved in June and July.
Chipotle said its traffic started growing again as the burrito chain exited the quarter and continued into July. Sweetgreen has seen “modest” improvement in its same-store sales so far into the third quarter, according to Neman.
And while Wingstop executives said that they’re still seeing weaker consumer demand, the chain is facing easier comparisons to last year’s performance.
Business
Two ships hit near Strait of Hormuz as fears grow of oil price rises

International shipping is said to have come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with fears of disruption already pushing up global oil prices.
Source link
Business
Khamenei dead, Middle East on edge: What will be the implications of Trump’s ‘Epic fury’ on stock markets, gold & oil? – The Times of India

The global markets are in for a phase of enhanced turmoil and uncertainty! The ongoing tensions in the Middle East after US and Israel’s strikes on Iran and Ali Khamenei’s death may have investors running for cover – looking for an asset class that is safer.During the night of February 27–28, the United States and Israel carried out joint aerial strikes on Iran as part of “Operation Epic Fury.” Statements by President Trump openly referring to regime change suggest that the confrontation could evolve into a prolonged campaign rather than remain a limited exchange, say market analysts at Franklin Templeton Institute.What does the situation mean for stock markets, energy markets (oil), gold and other asset classes? Here’s what Franklin Templeton Institute analysts have to say:From a market perspective, the key uncertainty is whether the conflict remains confined to direct military engagement or expands into disruptions affecting energy supplies and logistics networks, which would sustain a higher and more persistent risk premium.At the centre of the ongoing uncertainty from a global market and trade perspective is the Strait of Hormuz. While a complete blockade would carry severe consequences for Iran itself, the country has the capability to disrupt maritime traffic through tactics such as vessel harassment, seizures, drone activity, cyber operations, or the use of proxy forces.
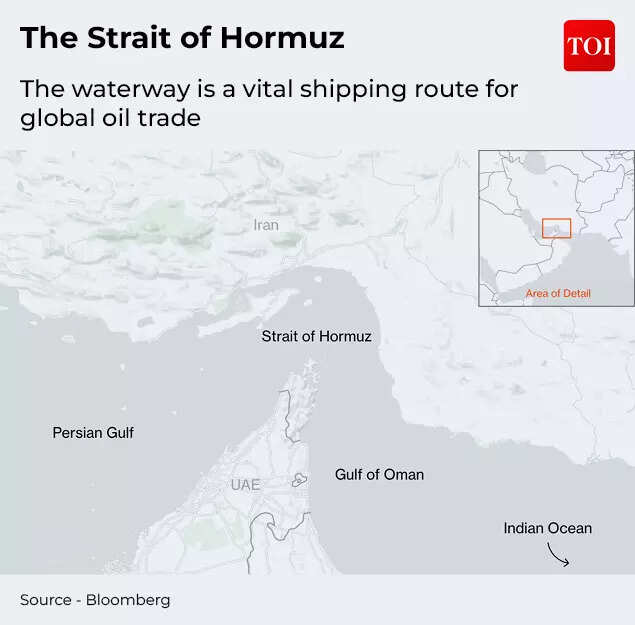
Strait of Hormuz
The most immediate economic impact is expected in energy markets, where crude oil and natural gas prices are likely to move higher, they say. Such actions, feel analysts, will keep geopolitical risk premiums at high levels. In 2024, approximately 20 million barrels per day moved through the Strait of Hormuz, which is around one-fifth of global petroleum liquids consumption. Even a limited interference – which can be caused by delays, rerouting, or isolated seizure – can push prices higher through increased risk perception well before any actual shortages emerge.Liquefied natural gas should not be overlooked in this context. Qatar has the world’s third-largest LNG export capacity, and roughly one-fifth of global LNG shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, largely consisting of Qatari exports. As a result, shipping risks in the region affect gas markets as significantly as oil markets.Also Read | US-Israel strikes on Iran: How will India be hit by Strait of Hormuz closure? ExplainedShipping expenses have already begun to rise, with insurance costs acting as a major driver. Insurers have started issuing cancellation notices and revising war-risk premiums for voyages in the Gulf region. Some routes have reportedly seen premium increases of up to about 50%, while earlier periods of tension recorded rises exceeding 60% on important trade corridors. These developments effectively tighten supply conditions even when production levels remain unchanged.The possibility of the conflict spreading across the region is increasing. Franklin Templeton Institute analysts are of the view that across global financial markets, the immediate response to such shocks is usually driven by adjustments in risk perception rather than by underlying economic changes. “The initial market reaction for this type of event would typically see Treasury yields move lower and equities lower—mostly a risk-premium repricing. Impacts on activity/earnings may be delayed and uneven. The US dollar reaction is not guaranteed; gold tends to benefit while bitcoin has been trading like a risk asset (i.e., down with equities), reinforcing that it’s not typically a reliable hedge/diversifier in geopolitical drawdowns,” say Franklin Templeton Institute analysts.However, they note that experience shows markets often come to view geopolitical disruptions as temporary. Initial spikes in risk premiums are frequently followed by the realization that the overall effect on corporate profitability is limited. The duration of the conflict, developments in shipping and insurance costs, and the eventual resolution will be more important than the initial headlines.“We would not yet label this a clean buy-the-dip setup—duration, shipping/insurance mechanics, and the endgame matter more than the first headline,” they say.From an investment perspective, the near-term outlook favours sectors linked to energy markets, as well as companies benefiting from higher shipping and insurance costs, along with defence-related industries, the analysts say. At the same time, caution is warranted toward emerging markets that depend heavily on energy imports and toward cyclical sectors sensitive to fuel and logistics costs, including airlines and certain industrial segments.“For protection, we prefer oil upside/volatility structures and selective gold exposure over broad equity shorts—the path will be driven more by shipping/insurance reality than by the new cycle,” they conclude.
Business
Crude oil prices in focus: OPEC+ increases output by 206,000 bpd amid Middle East tensions – The Times of India

OPEC+ on Sunday announced a higher-than-expected increase in oil production quotas, days after US and Israeli strikes on Tehran triggered Iranian retaliation across the Middle East, according to AFP.The oil producers’ group, which includes Saudi Arabia, Russia and several Gulf states affected by the escalation, said it had “agreed on a production adjustment of 206 thousand barrels per day”.“This adjustment will be implemented in April,” OPEC+ said in a statement.While the cartel did not directly refer to the Iran conflict, it cited “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals” as the rationale behind the output increase.The move comes amid heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, a region critical to global crude oil supply.
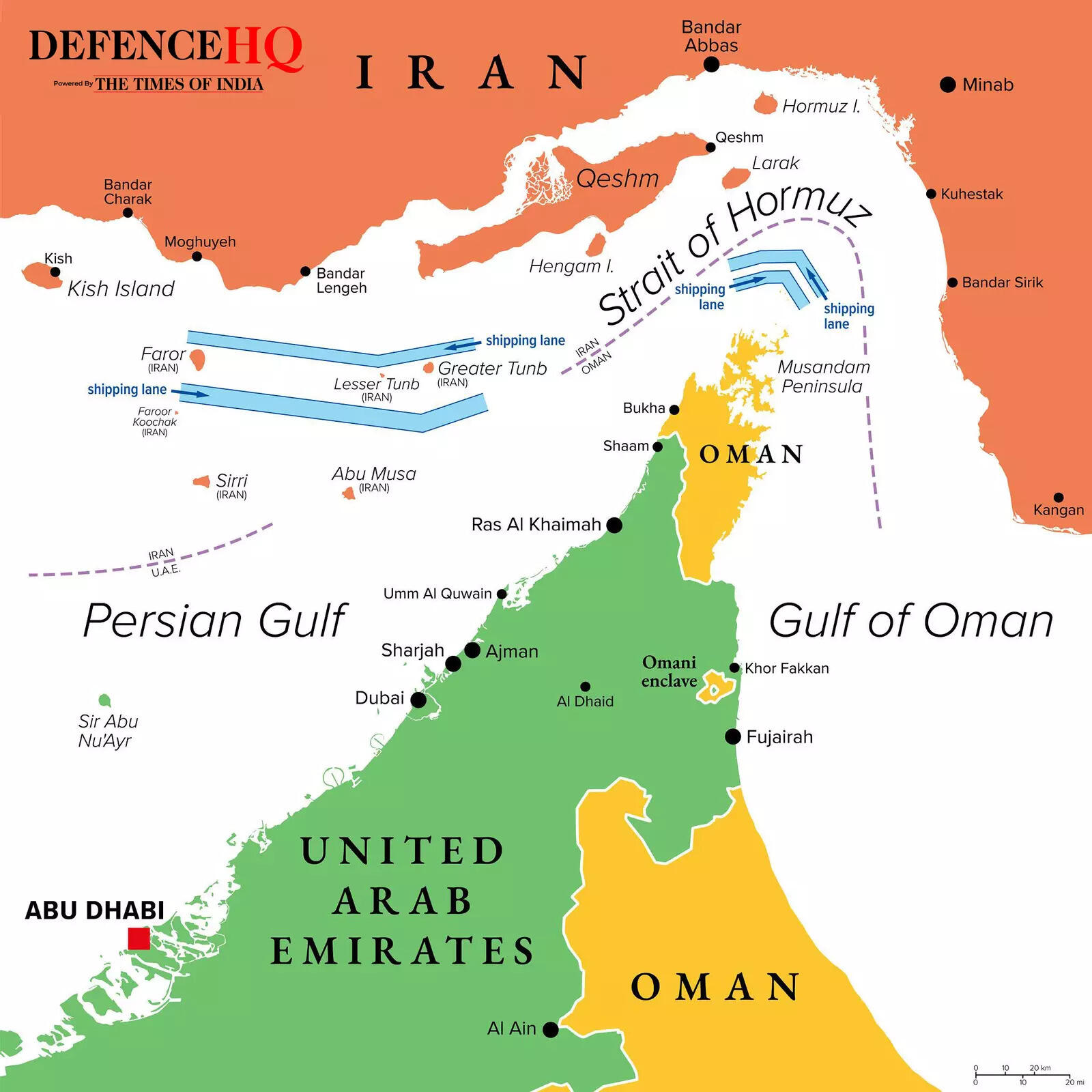
The announcement did not directly reference the outbreak of the Iran conflict, instead attributing the decision to “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals”.Before the meeting, analysts had projected a more modest increase of 137,000 barrels per day.However, Jorge Leon, an analyst at Rystad Energy, cautioned that the agreed hike may not be sufficient to offset the potential impact of escalating tensions on crude oil markets.Leon highlighted the risk of disruption in the Strait of Hormuz, a critical waterway through which nearly a quarter of the world’s seaborne oil supplies transit.Iran’s Revolutionary Guards have reportedly contacted vessels to declare the strait closed. Iranian state television on Sunday said an oil tanker attempting to “illegally” pass through the strait was struck and was sinking, broadcasting footage of a burning tanker at sea.“If oil cannot move through Hormuz, an extra 206,000 barrels per day does very little to ease the market,” Leon said, adding that “logistics and transit risk matter more than production targets right now”.He said the OPEC+ move “is unlikely to calm markets”, noting that “prices will respond to developments in the Gulf and the status of shipping flows, not to a relatively small increase in output.”Apart from Russia and Saudi Arabia, the V8 group includes Kuwait, Oman, Iraq and the United Arab Emirates — all of which were targeted by Iranian attacks for a second consecutive day on Sunday. Algeria and Kazakhstan are also part of the group.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThese Cheap Noise-Cancelling Sony Headphones Are Even Cheaper Right Now
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoSaturday Sessions: Say She She performs "Under the Sun"
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThe Supreme Court’s Tariff Ruling Won’t Bring Car Prices Back to Earth
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoViral monkey Punch makes IKEA toy global sensation: Here’s what it costs
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoFloyd Mayweather to come out of retirement again












