Business
Gaps in anti-laundering efforts: IMF | The Express Tribune

ISLAMABAD:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has observed that Pakistan is not effectively using data on the ultimate real owners of companies, creating hurdles in disrupting corruption-related laundering schemes and checking front companies from securing government contracts.
The global lender’s draft report on the Governance and Corruption Diagnostic Assessment revealed major flaws in the effective implementation of the country’s beneficial ownership regime.
The IMF found “little evidence of routine coordination” between the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP) and investigation agencies for exchanging and using beneficial ownership data in financial investigations.
However, Pakistani authorities disagreed with the IMF’s findings, stating that agencies were using beneficial ownership data, except in the case of Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Persons (DNFBPs).
Pakistan tightened its beneficial ownership rules about eight years ago as part of Financial Action Task Force (FATF) conditions. However, as in many other cases, implementation remains far below the desired goals.
The IMF stated that effective use of beneficial ownership information in financial investigations requires regular exchanges between the SECP, the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), commercial banks, money service providers, and investigation agencies.
The IMF’s diagnostic mission recommended that Pakistan institutionalise a multi-agency working group to review beneficial ownership data in support of corruption investigations.
The IMF noted that Pakistan’s beneficial ownership framework is an important foundational tool, but weaknesses in registry implementation, verification, enforcement, and inter-agency access reduce its impact.
“Addressing these challenges will be essential to ensuring that beneficial ownership transparency plays a meaningful role in the identification and disruption of corruption-related laundering schemes,” the global lender observed.
It added that access to accurate and timely beneficial ownership data is essential not only for detecting illicit financial flows but also for uncovering conflicts of interest in public procurement, particularly when public officials or their close associates have undisclosed stakes in bidding firms.
Pakistani authorities said that, as part of effective inter-agency coordination, the SECP has provided direct access to its beneficial ownership database to investigation agencies. They said the Financial Monitoring Unit (FMU) was regularly using the data to analyse suspicious transactions.
In 2018, the SECP directed companies to collect information about their real owners to address FATF concerns about transparency in company ownership structures. The directions had been given to uncover layers of secrecy hiding ultimate beneficial owners.
All companies with legal persons as members or shareholders are required to obtain and maintain information from their members and shareholders about the ultimate beneficial owners.
The minimum information required includes the owner’s full name, father’s or husband’s name, NIC/NICOP/passport number, nationality, country of origin, email address, usual residential address, the date on which the name was entered into the register, and the date and reason the person ceased to be the beneficial owner.
Section 453 of the Companies Act 2017 also requires every company officer to endeavour to prevent fraud and offences of money laundering, including predicated offences under the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010, in relation to the company’s affairs.
However, the IMF found serious gaps in the implementation of these laws and rules, hindering the disruption of illicit money flows.
Global bodies agree that collusive practices can only be mitigated by exposing front companies used to siphon public funds and by supporting fair competition in government contracting.
The IMF said that ensuring contracting authorities, integrity bodies, and investigative agencies can effectively access and cross-reference beneficial ownership data with procurement records is critical to advancing governance reform and restoring public trust.
The effectiveness of financial institutions and Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) in detecting and reporting corruption-linked transactions remains limited, the IMF stated.
Pakistan’s legal and regulatory framework requires reporting entities — including banks, money service businesses, and DNFBPs — to implement risk-based customer due diligence, conduct enhanced due diligence on politically exposed persons (PEPs), and file suspicious transaction reports (STRs). However, implementation is uneven and often inadequate in addressing high-risk areas associated with corruption.
Pakistani authorities said some state agencies were actively using the SECP’s online beneficial ownership database to enrich financial intelligence. The FMU continues to advocate improved access to beneficial ownership data for key stakeholders and stronger implementation of anti-money laundering obligations by reporting entities through targeted guidance, training, and inter-agency collaboration.
Financial institutions have made notable progress in applying risk-based customer due diligence and conducting enhanced due diligence on politically exposed persons (PEPs).
However, challenges remain, particularly in the DNFBP sector, where the level of technical capacity, compliance culture, and supervisory coverage vary, according to Pakistani authorities.
Business
Khamenei dead, Middle East on edge: What will be the implications of Trump’s ‘Epic fury’ on stock markets, gold & oil? – The Times of India

The global markets are in for a phase of enhanced turmoil and uncertainty! The ongoing tensions in the Middle East after US and Israel’s strikes on Iran and Ali Khamenei’s death may have investors running for cover – looking for an asset class that is safer.During the night of February 27–28, the United States and Israel carried out joint aerial strikes on Iran as part of “Operation Epic Fury.” Statements by President Trump openly referring to regime change suggest that the confrontation could evolve into a prolonged campaign rather than remain a limited exchange, say market analysts at Franklin Templeton Institute.What does the situation mean for stock markets, energy markets (oil), gold and other asset classes? Here’s what Franklin Templeton Institute analysts have to say:From a market perspective, the key uncertainty is whether the conflict remains confined to direct military engagement or expands into disruptions affecting energy supplies and logistics networks, which would sustain a higher and more persistent risk premium.At the centre of the ongoing uncertainty from a global market and trade perspective is the Strait of Hormuz. While a complete blockade would carry severe consequences for Iran itself, the country has the capability to disrupt maritime traffic through tactics such as vessel harassment, seizures, drone activity, cyber operations, or the use of proxy forces.
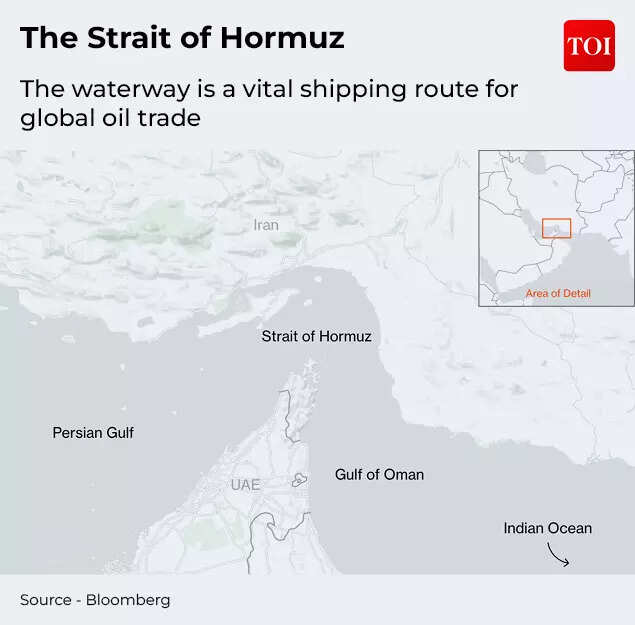
Strait of Hormuz
The most immediate economic impact is expected in energy markets, where crude oil and natural gas prices are likely to move higher, they say. Such actions, feel analysts, will keep geopolitical risk premiums at high levels. In 2024, approximately 20 million barrels per day moved through the Strait of Hormuz, which is around one-fifth of global petroleum liquids consumption. Even a limited interference – which can be caused by delays, rerouting, or isolated seizure – can push prices higher through increased risk perception well before any actual shortages emerge.Liquefied natural gas should not be overlooked in this context. Qatar has the world’s third-largest LNG export capacity, and roughly one-fifth of global LNG shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, largely consisting of Qatari exports. As a result, shipping risks in the region affect gas markets as significantly as oil markets.Also Read | US-Israel strikes on Iran: How will India be hit by Strait of Hormuz closure? ExplainedShipping expenses have already begun to rise, with insurance costs acting as a major driver. Insurers have started issuing cancellation notices and revising war-risk premiums for voyages in the Gulf region. Some routes have reportedly seen premium increases of up to about 50%, while earlier periods of tension recorded rises exceeding 60% on important trade corridors. These developments effectively tighten supply conditions even when production levels remain unchanged.The possibility of the conflict spreading across the region is increasing. Franklin Templeton Institute analysts are of the view that across global financial markets, the immediate response to such shocks is usually driven by adjustments in risk perception rather than by underlying economic changes. “The initial market reaction for this type of event would typically see Treasury yields move lower and equities lower—mostly a risk-premium repricing. Impacts on activity/earnings may be delayed and uneven. The US dollar reaction is not guaranteed; gold tends to benefit while bitcoin has been trading like a risk asset (i.e., down with equities), reinforcing that it’s not typically a reliable hedge/diversifier in geopolitical drawdowns,” say Franklin Templeton Institute analysts.However, they note that experience shows markets often come to view geopolitical disruptions as temporary. Initial spikes in risk premiums are frequently followed by the realization that the overall effect on corporate profitability is limited. The duration of the conflict, developments in shipping and insurance costs, and the eventual resolution will be more important than the initial headlines.“We would not yet label this a clean buy-the-dip setup—duration, shipping/insurance mechanics, and the endgame matter more than the first headline,” they say.From an investment perspective, the near-term outlook favours sectors linked to energy markets, as well as companies benefiting from higher shipping and insurance costs, along with defence-related industries, the analysts say. At the same time, caution is warranted toward emerging markets that depend heavily on energy imports and toward cyclical sectors sensitive to fuel and logistics costs, including airlines and certain industrial segments.“For protection, we prefer oil upside/volatility structures and selective gold exposure over broad equity shorts—the path will be driven more by shipping/insurance reality than by the new cycle,” they conclude.
Business
Crude oil prices in focus: OPEC+ increases output by 206,000 bpd amid Middle East tensions – The Times of India

OPEC+ on Sunday announced a higher-than-expected increase in oil production quotas, days after US and Israeli strikes on Tehran triggered Iranian retaliation across the Middle East, according to AFP.The oil producers’ group, which includes Saudi Arabia, Russia and several Gulf states affected by the escalation, said it had “agreed on a production adjustment of 206 thousand barrels per day”.“This adjustment will be implemented in April,” OPEC+ said in a statement.While the cartel did not directly refer to the Iran conflict, it cited “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals” as the rationale behind the output increase.The move comes amid heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, a region critical to global crude oil supply.
The announcement did not directly reference the outbreak of the Iran conflict, instead attributing the decision to “a steady global economic outlook and current healthy market fundamentals”.Before the meeting, analysts had projected a more modest increase of 137,000 barrels per day.However, Jorge Leon, an analyst at Rystad Energy, cautioned that the agreed hike may not be sufficient to offset the potential impact of escalating tensions on crude oil markets.Leon highlighted the risk of disruption in the Strait of Hormuz, a critical waterway through which nearly a quarter of the world’s seaborne oil supplies transit.Iran’s Revolutionary Guards have reportedly contacted vessels to declare the strait closed. Iranian state television on Sunday said an oil tanker attempting to “illegally” pass through the strait was struck and was sinking, broadcasting footage of a burning tanker at sea.“If oil cannot move through Hormuz, an extra 206,000 barrels per day does very little to ease the market,” Leon said, adding that “logistics and transit risk matter more than production targets right now”.He said the OPEC+ move “is unlikely to calm markets”, noting that “prices will respond to developments in the Gulf and the status of shipping flows, not to a relatively small increase in output.”Apart from Russia and Saudi Arabia, the V8 group includes Kuwait, Oman, Iraq and the United Arab Emirates — all of which were targeted by Iranian attacks for a second consecutive day on Sunday. Algeria and Kazakhstan are also part of the group.
Business
Cost Of Raising Kids: Raising kids in this economy: To DINK or not? Why more Indian couples are rethinking parenthood – The Times of India

Raising a child in today’s economy isn’t just about love, care, and dreams. It’s more about smart planning and careful budgeting. Even before the baby is born, mamma and papa are already thinking ahead, carefully categorizing their everyday savings to secure their child’s future.As the cost of raising babies into full fledged adults continues to climb, many couples are hitting a pause button on parenthood and embracing the DINK — Double Income, No Kids — lifestyle. Once viewed largely as a Western trend, the DINK concept has now entered everyday vocabulary and is gaining ground in India, with a growing number of couples choosing to remain child-free.

Driving this shift is a mix of financial realities, emotional considerations and environmental concerns that is steadily reshaping how modern couples approach the idea of parenthood.
Why are so many couples choosing not to have children?
A world too harsh For many, the decision not to have children is shaped by the harsh realities of the world. “The air is terrible and life already feels quite demanding,” Nimish Rastogi, an entrepreneur, told TOI. A video journalist working in Delhi raised similar concerns and said, “resources are depleting, everything is only going to get costlier, and institutions are in decline. For months in Delhi-NCR, we can’t even breathe because of pollution, and the rest of the year, we’re dying from the heat. How do you raise a child in a world like this?”Balancing kid and work — Herculean job!For many working couples, raising a child can feel like an almost impossible balancing act. “Juggling work, home and a child can be taxing, and realistically you need a certain level of financial comfort to afford the kind of support that lets you enjoy everything without compromising too much on your own interests and lifestyle,” Nimish said. Anurag Kumar, assistant editor, added that the decision is also influenced by daily time and work pressure as “managing day-to-day work while keeping the household running is already demanding.”

Family plays a roleFor many, raising a child without strong family support feels overwhelming. “Unless there is strong support from family, raising a child on your own can feel almost impossible to balance,” Anurag said. Others find the idea of constant oversight intrusive. “Having a whole proverbial village breathing down my neck is not good for my mental health,” explained the video journalist, who did not wish to be named, that the concept clashes with the life they currently have.Personal preferencesFor many couples, maintaining personal freedom and lifestyle balance plays a key role in the decision to remain child-free. “We genuinely like having our freedom…right now, this kind of lifestyle feels fulfilling and balanced for us,” Nimish added. Anurag summed it up, saying, “The choice to have a child ultimately depends on the couple, their vision for life, where they stand at present, and how they see their future unfolding.”Education — a costly affairFor many, the decision not to have children is increasingly driven by practical considerations, citing the rising costs of childcare, schooling, healthcare, and housing becoming hard to ignore. “I went to a Catholic convent school for my schooling and my quarterly tuition fees was Rs 1800. Quarterly! What do you get for Rs 1800 today?” the video journalist told TOI. “In a volatile economy, anything can happen. I lost my job during COVID-19 for four months. Imagine if I had a child in school then — it would have been even harder,” she further added, throwing light on how unpredictable costs and economic uncertainty make the decision to have children a major financial consideration.Nimish added, “Education is so expensive now, healthcare costs are rising, and even basic things like good schools, extracurricular activities, childcare and daily expenses add up quickly.” For some, however, finances are only part of the equation. As Anurag said, “Finances are definitely a factor, but not the decisive one.”

How much does it actually cost to raise a child?
Raising a child from conception until the age of 21 costs an estimated Rs 74.3 lakh — and that’s without factoring in inflation.Rohit Saran explains in his book ‘100 Ways to See India: Stats, Stories, and Surprises’ that the total expense rises to approximately Rs 1.16 crore when adjusted for a 3% annual inflation rate. At a 6% inflation rate, the figure climbs even higher, reaching nearly Rs 1.83 crore. Couples today often find themselves stuck between two equally important dreams. Imagine you’ve finally saved up Rs 25–30 lakh for the down payment on a bigger 3BHK in a better neighbourhood, closer to work, with more space and security. But at the same time, you know that sending your child abroad for a master’s degree could easily cost Rs 40–60 lakh.So the question becomes real: do you upgrade your living standard now, or park that money in a fund that might one day pay for tuition fees in London or New York? For many families, these aren’t hypothetical situations — they’re monthly conversations at the dining table. A government official shared, “I’ve started a Voluntary Provident Fund for my daughter so that over the years, enough money will build up for her higher studies, learning new skills, or even starting her own business. I want her to have the freedom to chase her dreams without financial limits.” These decisions aren’t just about lump sums, they trickle down into everyday spending, shaping how families allocate resources across different categories. From education and housing to entertainment, clothing, food, transportation, and healthcare, every rupee is carefully planned to balance current needs with long-term goals.

Raising a child goes beyond planned savings, their needs often reshape how families earn, spend, and prioritize money. Vacations, lifestyle upgrades, and even retirement plans are adjusted to give children the best opportunities. As a parent shared, “Sacrifice is part of being a parent. When you know your child needs a high-end laptop to study comfortably, you don’t dwell on your slow phone or the winter vacation you had planned, it’s not even a question.” Meanwhile, Swasti Choudhary, mother of a 2 year old, explained, “having both parents earning definitely makes a big difference. When I found out I was pregnant, my husband and I created a full budget plan. With both of us earning, the risk from sudden financial emergencies is much lower. That said, it comes with challenges. We constantly ensure that both of us are present for our son. Leaving our jobs isn’t an option — it would be a major setback for the family.”
Spending on kids — A bigger picture
EducationEducation alone accounts for more than half of the total cost of raising a child. At least 59% of overall childcare expenses are directed towards education. Think about it — school admissions, annual fees, uniforms, books, private coaching…year after year, these costs quietly add up, keeping parents on their toes and always planning the next step. And careful planning doesn’t end the moment their kids graduate — it continues with competitive exams, skill-building classes, technology needs, and even the possibility of studying abroad. Of all the expenses parents manage, education consistently emerges as the largest and most demanding category.HousingAbout 10% of child-rearing expenses go towards housing, as many parents upgrade to larger homes in safer, better-connected neighbourhoods. A government officer shared that he moved to a bigger flat before his daughter was born to ensure a child-friendly environment. “Moreover, since my job requires frequent transfers, I’m planning to settle my family near the NCR so she has access to all the major educational institutions and can choose freely. It will be expensive, yes, but it’s a financially sustainable decision that will benefit in the long run,” he further added.Entertainment Nearly 9% of the total child-rearing cost goes towards entertainment — and this share tends to rise sharply during the teenage years. What begins as spending on toys and birthday parties in early childhood gradually shifts to bigger expenses like smartphones, laptops, hobby classes, sports coaching, movie outings, and holidays with friends. For instance, a simple 16th birthday celebration at a cafe, combined with gifts and decorations, can easily cost Rs 25,000–40,000. Add in a new phone for school and social use, music or dance classes, and a yearly trip with friends, and entertainment quickly turns into a regular and often overlooked expense.ClothingClothing alone accounts for around 6% of the total cost of raising a child, reflecting the need to regularly replace everyday wear, school uniforms, shoes, and seasonal outfits as children grow.
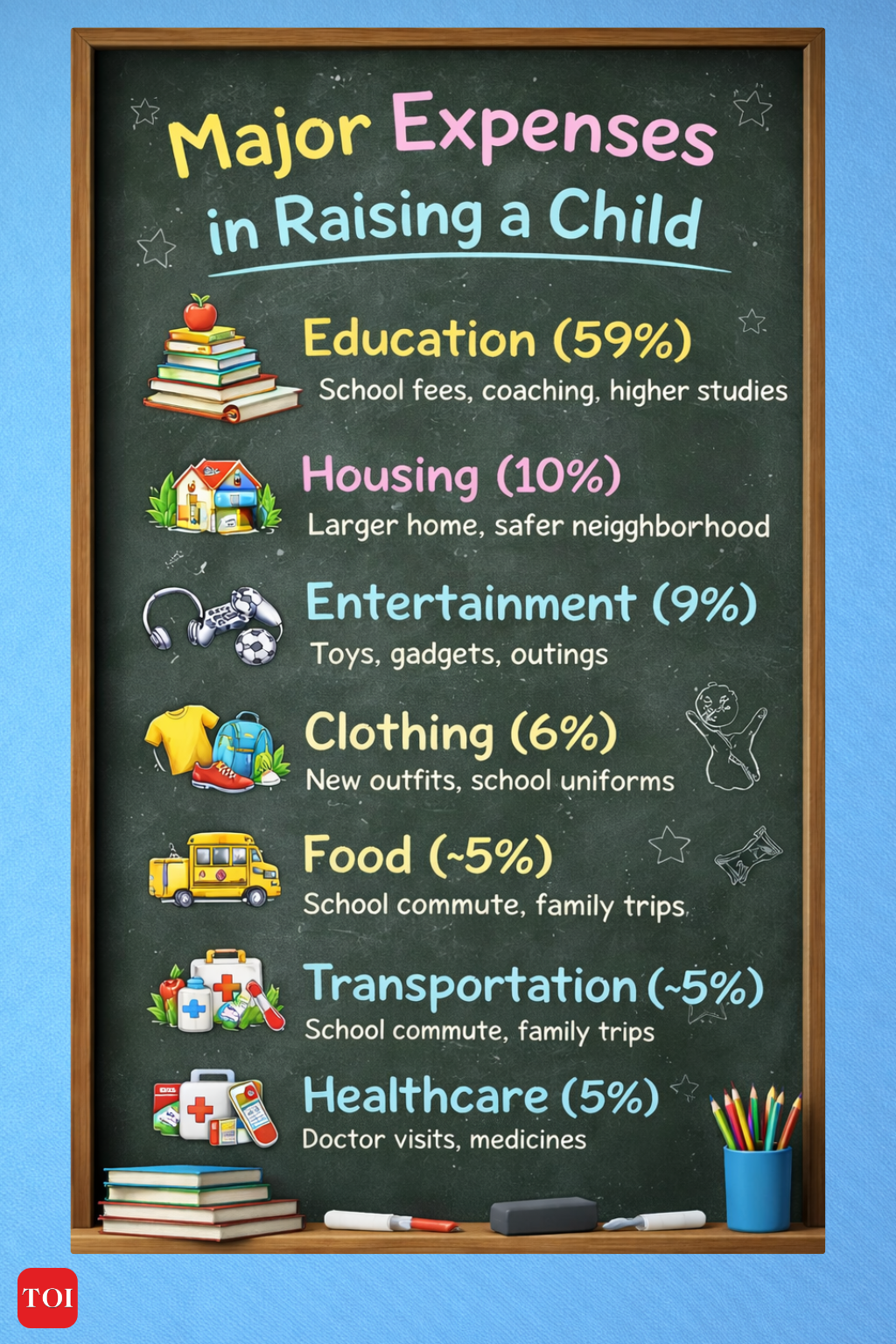
Education: the biggest slice of family expenses
According to the CMS Education Survey, part of the 80th round of the National Sample Survey (NSS) 2025, households across India are spending significantly on school education. Government vs private schooling: A sharp cost divideGovernment schools still enroll most students in India — 55.9% nationwide, 66% in rural areas, and 30% in cities. But the cost of education varies widely. Households spent an average of Rs 2,863 per student on school education in government schools, while spending in non-government schools cost nine times more, at Rs 25,002. Course fees are the biggest expense, with urban families paying Rs 15,143 and rural families Rs 3,979 on average. Textbooks, stationery, uniforms, and transport add further costs, showing that “free” education often still comes with a price.Coaching and tuition cultureBeyond school fees, private coaching and tuition are emerging as parallel expenses. Nearly 27% of students nationwide are enrolled in private coaching — 30.7% in urban areas and 25.5% in rural regions.Urban families spend an average of Rs 3,988 annually on coaching per student, compared to Rs 1,793 in rural areas. At the higher secondary level, the gap widens sharply — Rs 9,950 in urban India versus Rs 4,548 in rural areas. Nationally, coaching costs rise with grade levels, from Rs 525 at pre-primary to Rs 6,384 at higher secondary.Study abroadAccording to a report by HSBC titled Quality of Life Report 2024, 90% of affluent Indian parents intend to fund their child’s overseas education. However, the cost of a three- or four-year international degree in destinations like the US or UK could consume up to 64% of parents’ retirement savings .The report also notes that 40% of parents expect their children to take student loans, 51% hope for scholarships and 27% would consider selling assets to fund overseas studies .

Fur babies over babies: A growing DINK trend
As more couples rethink what a “perfect” family means to them, many are opting for pets instead of children. For these couples, the choice is both practical and personal — offering companionship without the financial and lifestyle pressures that come with raising a child.With the rising costs of raising children, pets, particularly dogs, are increasingly viewed as a more manageable and predictable responsibility. “Once you get a dog and it’s healthy, you have a fairly fixed cost for its lifetime. Sure, you buy toys or treats, but that’s it. A child? The costs just keep growing. It never stops. Everything is so expensive!” the video journalist told TOI.While more couples are embracing the DINK lifestyle, broader social expectations still lean toward parenthood. Anurag said, “Most of my married friends are planning or already having children. I’m the only one who chose to have a dog instead.”“Among our friends, some have children, but I’ve noticed a growing number of couples choosing pets or delaying plans for kids. People are thinking more consciously about the life they want rather than just following the traditional path,” Nimish added, further sharing the flexibility that pets offer over having kids. “We genuinely value our freedom. We love travelling, making spontaneous plans, and spending time with friends and our dogs, who are basically our babies. For us, this lifestyle feels fulfilling and balanced right now.”
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoUS Top Court Blocks Trump’s Tariff Orders: Does It Mean Zero Duties For Indian Goods?
-

 Fashion1 week ago
Fashion1 week agoICE cotton ticks higher on crude oil rally
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoThe White Lotus” creator Mike White reflects on his time on “Survivor
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoBrett Favre blasts NFL for no longer appealing to ‘true’ fans: ‘There’s been a slight shift’
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoUS Supreme Court strikes down Trump’s trade tariff measures













