Politics
Netherlands sets global standard in flood defence and water management
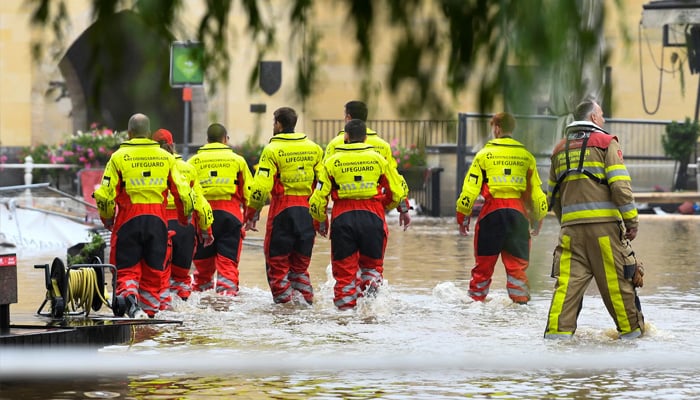


The Netherlands has emerged as a world leader in protecting land from rising waters, investing up to 1.3 billion euros each year to maintain an extensive system of dikes, polders, canals, windmills, concrete barriers and embankments that keep floods at bay, The News reported citing a research.
Moreover, artificial dwelling hills or Terpins have also been built to increase the land elevation.
Similar to Bangladesh, the Netherlands has also created a scheme that alerts citizens of possible floods 24 hours before the otherwise uncontrollable waters hit the country.
The anti-flood system they have built over decades is on a scale unmatched anywhere else in the world.
The Dutch have also built a giant sea gate guarding the port of Rotterdam, the largest port in Europe, and a c rucial hub for industries of all sorts.
A media house maintained: “The gate has two curved arms; each as tall and twice as heavy as the Eiffel Tower. When needed, they swing out into the water to lock together and sink to the bottom, forming a 22-meter-high wall against the sea. The barrier is one of the largest moving structures on Earth; its two ball-and-socket joints, anchored in the embankment on either side of the canal, weigh 680 tonnes each.”
From 1962 until 2004, the 31,500-acre Rotterdam was the world’s busiest port by annual cargo tonnage. It was overtaken first in 2004 by the port of Singapore, and later by Shanghai and other very large Chinese seaports.
In May 2019, global investors had enthusiastically embraced a national Netherlands 5.98 billion-Euro Green Bond designed to fund projects to cope with current and future climate change impacts and an advanced low-carbon economy.
Much of the bond focused on using coastal and river ecosystems as a safeguard for negative climate impacts such as high flood risk.
Investors responded to the bond immediately, oversubscribing the issuance by more than 15.2 billion Euros!
Although global warming can overwhelm the measures the Netherlands has taken to control floods, the risk of these water-related disasters has been reduced from once every 100 years to once every 1,250 years.
The region has a long history of devastating floods that continually reshape the land. For more than 1,000 years the residents of this region have devised ways to reclaim land from encroachment by the sea.
The Rhine, Meuse and Schelde are Holland’s three chief rivers.
The densely-populated Netherlands or Holland is known for its low elevation and approximately two-thirds of its area is vulnerable to flooding.
While 15 million people in the Netherlands live below the sea level, the river Rhine and its tributaries, the Meuse and the Mosel, have often attacked Holland, Belgium and Luxembourg.
The first river dikes had appeared near the river mouths in the 11th century, where incursions from the sea added to the danger from high water levels on the river.
The 17th and 18th centuries were a period of many infamous river floods resulting in much loss of life. They were often caused by ice dams blocking the river. Land reclamation works, large willow plantations and building in the winter bed of the river all worsened the problem.
The “Encyclopedia Britannica” states: “The first Dutch food in 1287 had caused more than 50,000 casualties. A significant percentage of the country’s population perished in the disaster, and it has been rated as one of the most destructive floods in recorded history. Called the St Lucia flood, this event also created direct sea access for the village of Amsterdam, allowing its development into a major port city.”
The 1421 floods had killed up to 10,000 people.
In more recent history, February 1953 had seen one of the biggest natural disasters hitting the Netherlands ever, killing 2400 humans.
Around 770 square miles of southern Holland were inundated, forcing tens of thousands to flee.
Many were overtaken by the icy waters as more and more flood walls failed. The storm also devastated parts of England, Belgium and Germany.
Urbanisation is one of the major causes of flooding in Netherlands.
The urban population here accounts for 82.9% of the total population. A lot of buildings, roads, and cities have thus been built over the course of centuries, leading to destruction of vegetation, hence reducing the interception of rainfall when a storm is to occur.
Additionally, the excessive use of tar and cement to pave roads and sidewalks inhibit water from infiltrating the soil, which increases the chances of surface runoff.
These artificial structures are impermeable, and water is forced to flow back into the ocean through surface runoff, increasing the peak discharge in the area. Due to this, the lag time for water to flow back into the ocean has decreased, increasing the chances of flooding.
Due to land reclamation, areas close to the shoreline become more prone to coastal waves. Erosion takes place resultantly and the fast-sinking land leads to floods.
And then for the sake of urbanisation and providing land for agriculture and ploughing, deforestation has taken place.
Being the world’s second largest exporter of agricultural products, agriculture plays an immense role in the Netherlands’ economy. Presently, over 70% of the country’s land is used for agricultural purposes.
The Guardian reported that the low-lying Netherlands has been fighting back water for more than 1,000 years, when farmers built the first dykes.
“Windmills have also been pumping the stuff off the land since the 14th century. One of the most densely populated countries on the planet, 60% of the Netherlands is vulnerable to flooding, and its peat-rich agricultural soil is subsiding even as climate change is raising sea levels. The country’s universities are producing some of the world’s best water engineers and managers and it is exporting its expertise abroad; the Dutch government has advised on water governance projects in China, Africa and Australia,” the report stated.
Meanwhile, The British newspaper revealed “there are no financial packages for people who have to move.”
It quoted a government official as saying: “They get the market value of their house and that is all. We will help them find another place, but not financially. The only thing we do is to make sure that they do not lose money.”
Politics
Key Iranian figures martyred in US-Israel military strikes
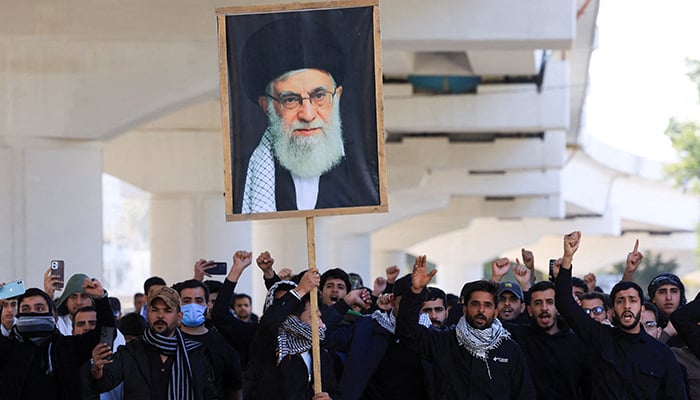


A number of Iranian senior leaders, including Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, have embraced martyrdom in the “unprovoked and unwarranted” airstrikes by Israel and the United States.
As crowds gathered in Tehran, explosions rang out, and the Israeli military announced that it was again striking targets in the heart of the city — as more blasts were heard in Jerusalem, Riyadh, Dubai, Doha and Manama.
Iran’s President Masoud Pezeshkian declared Khamenei’s assassination a “declaration of war against Muslims” and warned: “Iran considers it its legitimate duty and right to avenge the perpetrators and masterminds of this historic crime.”
Iranian state media have confirmed the killing of several senior figures:
1. Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, supreme leader of Iran
2. Ali Shamkhani, representative of the Supreme Leader in the Supreme Defence Council
3. General Abdolrahim Mousavi, Iran’s Armed Forces chief of staff
4. Major General Mohammad Pakpour, commander-in-chief of the Islamic Revolution Guards Corps (IRGC)
5. Aziz Nasirzadeh, Minister of Defence
6. Gholamreza Rezaian, police intelligence chief of Iran
Separately, the daughter, son-in-law, and granddaughter of Ali Khamenei also embraced martyrdom in the US and Israeli airstrikes.
Politics
US-Iran conflict disrupts thousands of flights as travel chaos deepens

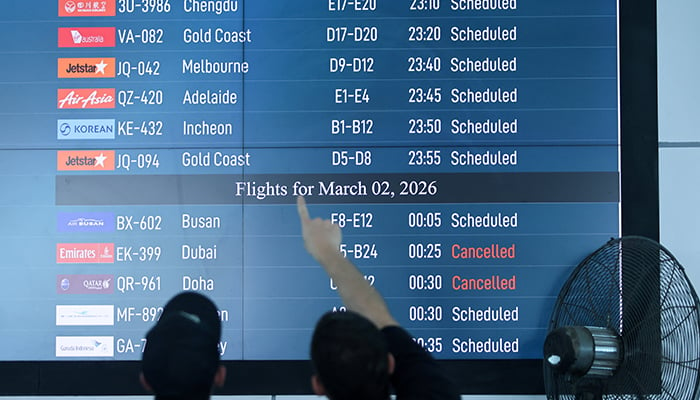
- Middle Eastern airport hubs remain closed or restricted.
- Airlines reroute or cancel flights, affecting global schedules.
- Risk of prolonged disruption due to regional conflicts.
DUBAI: Global air travel remained heavily disrupted on Sunday as continued air strikes kept major Middle Eastern airports, including Dubai, the world’s busiest international hub, closed in one of the sharpest aviation shocks in recent years.
Key transit airports including Dubai and Abu Dhabi in the UAE, and Doha in Qatar, were shut or severely restricted as much of the region’s airspace remained closed, with the Gulf grappling with uncertainty after U.S. and Israeli strikes killed Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei on Saturday.
Israel said it launched another wave of strikes on Iran on Sunday, while loud blasts were heard for a second day near Dubai and over Doha, after Iran launched retaliatory air attacks on the neighbouring Gulf states.
Dubai International Airport sustained damage during Iran’s attacks, while airports in Abu Dhabi and Kuwait were also hit. Thousands of flights have been affected across the Middle East since the U.S. first launched attacks on Iran on Saturday, according to data on FlightAware, a flight tracking platform.
Ripple effects
The airport closures have rippled far beyond the Middle East. Dubai and neighbouring Doha sit at the crossroads of east-west air travel, funnelling long-haul traffic between Europe and Asia through tightly scheduled networks of connecting flights.
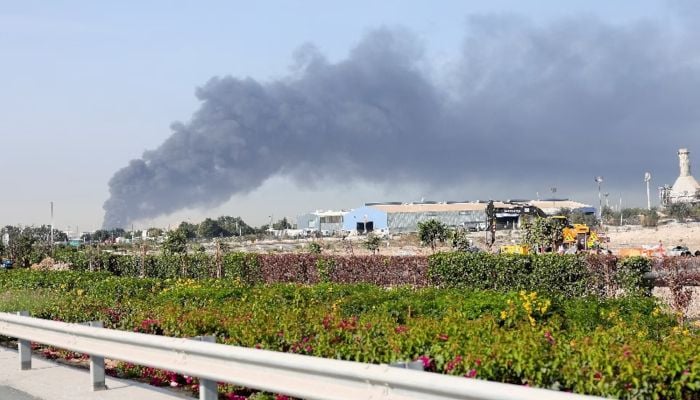

With those hubs idle, aircraft and crews remained stranded out of position, disrupting airline schedules worldwide.
“It’s the sheer volume of people and the complexity,” said UK-based aviation analyst John Strickland.
“It is not only customers, it is the crews and aircraft all over place.”
Airlines across Europe, Asia and the Middle East cancelled or rerouted flights to avoid closed or restricted airspace, lengthening journeys and driving up fuel costs. The disruption has been intensified by the loss of Iranian and Iraqi overflight routes, which had grown more important since the Russia-Ukraine war forced airlines to avoid both countries’ airspace.
The Middle East airspace closures were squeezing airlines into narrower corridors, with fighting between Pakistan and Afghanistan adding a further risk, said Ian Petchenik, communications director at Flightradar24.
“The risk of protracted disruption is the main concern from a commercial aviation perspective,” Petchenik said.
“Any escalation in the conflict between Pakistan and Afghanistan that results in the closure of airspace would have drastic consequences for travel between Europe and Asia.”
Middle East flights halted
Airspace over Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Israel, Bahrain, the UAE and Qatar remained virtually empty, maps by flight-tracking service Flightradar24 showed, and air strikes kept major Middle Eastern airports, including Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Doha shut or severely restricted.
Below is the latest on flights listed by airline in alphabetical order:
Aegean Airlines
Greece’s largest carrier suspended flights to and from Tel Aviv in Israel, Beirut in Lebanon and Erbil in Iraq until March 2.
Air Astana
The group cancelled all flights to the Middle East through March 3.
Air Canada
The airline said it has cancelled flights from Canada to Israel until March 8 and flights to Dubai until March 3.
Air Europa
The Spanish airline cancelled its flights to Tel Aviv on Sunday and Monday and is monitoring the situation to assess operations from Tuesday.
Air France KLM
Air France cancelled flights to and from Tel Aviv in Israel and Beirut in Lebanon for Saturday.
Its Dutch arm KLM said late on Saturday that this weekend’s flights to and from Dubai, Dammam and Riyadh have been cancelled. It had already brought forward suspension of its Amsterdam–Tel Aviv service to Saturday.
Air India
The carrier cancelled flights scheduled for Sunday from Delhi, Mumbai and Amritsar to London, New York, Chicago, Toronto, Frankfurt and Paris. It added that more flights to London, Birmingham, Amsterdam, Zurich, Milan, Vienna, Copenhagen and Frankfurt had been cancelled.
Azerbaijan Airlines
The airline has suspended flights to and from Dubai, Doha, Jeddah and Tel Aviv.
British Airways
IAG-owned British Airways said it has cancelled flights to Tel Aviv and Bahrain until March 3 and its flight to Amman on Saturday.
Cathay Pacific
Hong Kong’s Cathay Group, parent of Cathay Pacific Airways, suspended operations in the region, affecting passenger flights to and from Dubai and Riyadh, as well as freighter service at Al Maktoum airport. That is Dubai’s second airport after Dubai International Airport, the primary hub that handles most passenger traffic.
Emirates
Owing to multiple regional airspace closures, Emirates has suspended all operations to and from Dubai until 3pm UAE time on March 2.
Etihad
The UAE’s Etihad said flights scheduled to depart Abu Dhabi were suspended until 2pm local time on Sunday.
Flydubai
The airline said it had temporarily suspended all flights to and from Dubai until 3pm local time on Sunday.
Iberia Express
The Spanish airline owned by Iberia Group cancelled a flight to Tel Aviv scheduled for Saturday at 5pm local time.
IndiGo
IndiGo, India’s biggest airline, said it had extended a temporary suspension of select international flights using Middle East airspace until Monday.
ITA Airways
ITA Airways suspended flights to and from Tel Aviv and said it would not use the airspace of Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq and Iran until March 7. Flights to and from Dubai were suspended until March 1.
Japan Airlines
Japan Airlines cancelled a flight on Saturday from Tokyo Haneda to Doha as well as a return flight on March 1, Nikkei said.
LOT Polish Airlines
The airline suspended flights to Tel Aviv until March 15 and cancelled flights to Dubai and Riyadh until March 2.
Lufthansa
The German airline flights to and from Tel Aviv in Israel, Beirut in Lebanon and Oman until March 7 and flights to and from Dubai on Saturday and Sunday.
It also said it would not fly through Israeli, Lebanese, Jordanian, Iraqi and Iranian airspace until March 7.
Norwegian Air
The Nordic airline suspended all flights to and from Dubai until March 4, a company spokesperson said. The carrier did not suspend flights to Tel Aviv in Israel or Beirut in Lebanon because these destinations are only active in summer, he added.
Pegasus Airlines
The airline said that flights to Iran, Iraq, Jordan and Lebanon were cancelled up to and including March 2.
Qatar Airways
The airline said flights remain temporarily suspended owing to the closure of the Qatari airspace. It will provide a further update by 9am local time on Monday.
Scandinavian Airlines
The airline told Reuters it had suspended its flight to Tel Aviv from Copenhagen on Saturday. No decision had been made regarding flights on later dates.
Turkish Airlines
The airline cancelled flights to Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates and Oman on Saturday and flights to Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Iran and Jordan until March 2.
Virgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic said it will temporarily avoid Iraqi airspace, resulting in some pre-planned rerouting of flights and has cancelled its VS400 service from London Heathrow to Dubai on Saturday.
Wizz Air
The Hungarian carrier halted flights to and from Israel, Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Amman with immediate effect until March 7.
It added that operational decisions would continue to be reviewed and the flight schedule could be adjusted as the situation evolves.
Politics
CIA intel guided strikes that martyred Iran supreme leader: NYT
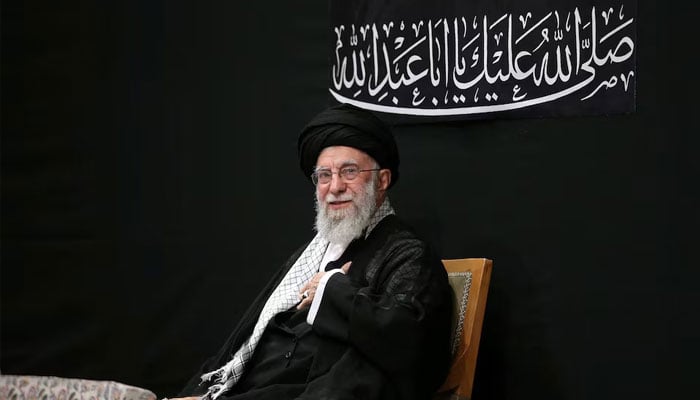


CIA intelligence indicating Ayatollah Ali Khamenei would attend a meeting of top Iranian officials helped guide strikes in a US and Israeli attack that killed Iran’s supreme leader, the New York Times reported Sunday.
Khamenei was martyred in the strikes on capital Tehran, Iranian state media confirmed on Sunday, after the US and Israel vowed to seek regime change in the Islamic republic.
The American intelligence agency had been tracking Khamenei for months, the Times reported, citing people familiar with the operation, and learned that a meeting of top Iranian officials was set for Saturday morning at a leadership compound in the heart of Tehran.
Washington and Tel Aviv originally planned to launch strikes on Iran at night, but officials adjusted the plan based on the CIA intelligence, according to the Times.
The US gave the information to Israel, who planned to carry out the attack on Iranian leadership, the newspaper reported.
The operation began about 6am in Israel (0400 GMT), and long-range missiles struck the compound about 9:40am, the Times said.
Senior Iranian national security officials were in one building at the compound, and Khamenei was in a nearby building.
In addition to Khamenei, two top Iranian military leaders were killed in the bombing: the chief of the Revolutionary Guards, General Mohammad Pakpour, and another top security adviser, Ali Shamkhani, Iran’s judiciary confirmed.
Iran has since retaliated, with reported strikes across the Gulf, including in the Emirati capital Abu Dhabi and near regional US military bases, as the threat of a larger regional conflict grows.
US President Donald Trump, meanwhile, has said the American military’s bombing will continue “as long as necessary.”
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoUS Top Court Blocks Trump’s Tariff Orders: Does It Mean Zero Duties For Indian Goods?
-

 Fashion1 week ago
Fashion1 week agoICE cotton ticks higher on crude oil rally
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoThe White Lotus” creator Mike White reflects on his time on “Survivor
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoBrett Favre blasts NFL for no longer appealing to ‘true’ fans: ‘There’s been a slight shift’
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoViral monkey Punch makes IKEA toy global sensation: Here’s what it costs
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping






