Business
Casino Math Can Power Your Portfolio: How Investors Can Win The Risk–Reward Game

Last Updated:
Winning more trades doesn’t mean winning more money. Alok Jain says long-term success comes from casino math—small losses, big winners
Casino Math
Investors often fixate on being “right” in the stock market by chasing the highest possible number of winning trades. But according to Alok Jain, founder of Weekend Investing, true long-term success in the markets comes from a counterintuitive principle: casino math. Addressing investors, Jain said the same probability-driven logic that enables casinos to earn billions can also help individuals build stronger and more profitable portfolios.
To explain the idea, Jain began with how casinos operate despite occasionally paying out massive jackpots. “A 25-year-old software engineer wins $39 million after betting just $100. Someone else wins $3 million on a $3 bet. Yet casinos continue to thrive because they focus on managing risk and reward—not on win rates,” he said.
In a typical setup, a casino might allow players to win seven out of 10 games. Even with that apparent disadvantage, the casino still profits because its losses are small while its gains are large. For instance, if the casino wins three rounds earning ₹100 each (₹300 total) but loses seven rounds losing ₹30 per round (₹210), it still makes a profit of ₹90. “The math defies intuition,” Jain explained, “but this is the essence of risk–reward.”
He then translated this concept into personal investing using a comparison between two investors—Ram and Sham. Ram wins 75% of his trades but settles for small gains while suffering large losses. Sham, in contrast, wins only 25% of his trades, but his winners are large and his losses are tightly controlled. At the end of the year, Ram ends up with just a 5% return, while Sham earns 13%. “The investor with more losing trades actually makes more money. That’s the power of reward overpowering risk,” Jain noted.
Jain said many investors behave like Ram because of loss aversion, a behavioural bias where losses hurt far more than equivalent gains feel good. This leads people to hold on to losing stocks in the hope of recovery, while booking profits too early on winning positions. “We deceive ourselves,” he said. “A stock falling from ₹100 to ₹60 is treated as temporary. Investors convince themselves it will bounce back, even as the damage keeps increasing.”
The impact of deep losses can be severe, Jain warned. A 50% fall requires a 100% gain just to recover. Falling another 30–40% pushes investors into an almost unrecoverable “ditch.” The core principle, he stressed, is simple: cut losses early and let winners run.
Jain also shared real data from a 242-trade systematic momentum strategy. Even though losing trades were higher than winning ones (52% losers versus 48% winners), the average winning trade delivered 25% returns, while average losses were capped at 9%. A handful of multi-bagger stocks—posting gains of 144%, 219% and even 298%—accounted for most of the portfolio’s overall performance. “Just like the Pareto principle, 20% of trades generate 80% of the returns,” he said.
The central takeaway, Jain emphasized, is that a high win rate does not guarantee profitability—risk–reward discipline does. “Don’t cling to losing stocks. Don’t fear rising stocks. Use stop-losses, churn smartly and allow the math to work in your favour,” he advised.
He urged investors to introspect on their behavioural biases and adopt systematic investing approaches that prioritise survival, consistency and large winners—rather than chasing bragging rights based on hit rates alone.

Aparna Deb is a Subeditor and writes for the business vertical of News18.com. She has a nose for news that matters. She is inquisitive and curious about things. Among other things, financial markets, economy, a…Read More
Aparna Deb is a Subeditor and writes for the business vertical of News18.com. She has a nose for news that matters. She is inquisitive and curious about things. Among other things, financial markets, economy, a… Read More
November 30, 2025, 10:58 IST
Read More
Business
Two ships hit near Strait of Hormuz as fears grow of oil price rises

International shipping is said to have come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with fears of disruption already pushing up global oil prices.
Source link
Business
Khamenei dead, Middle East on edge: What will be the implications of Trump’s ‘Epic fury’ on stock markets, gold & oil? – The Times of India

The global markets are in for a phase of enhanced turmoil and uncertainty! The ongoing tensions in the Middle East after US and Israel’s strikes on Iran and Ali Khamenei’s death may have investors running for cover – looking for an asset class that is safer.During the night of February 27–28, the United States and Israel carried out joint aerial strikes on Iran as part of “Operation Epic Fury.” Statements by President Trump openly referring to regime change suggest that the confrontation could evolve into a prolonged campaign rather than remain a limited exchange, say market analysts at Franklin Templeton Institute.What does the situation mean for stock markets, energy markets (oil), gold and other asset classes? Here’s what Franklin Templeton Institute analysts have to say:From a market perspective, the key uncertainty is whether the conflict remains confined to direct military engagement or expands into disruptions affecting energy supplies and logistics networks, which would sustain a higher and more persistent risk premium.At the centre of the ongoing uncertainty from a global market and trade perspective is the Strait of Hormuz. While a complete blockade would carry severe consequences for Iran itself, the country has the capability to disrupt maritime traffic through tactics such as vessel harassment, seizures, drone activity, cyber operations, or the use of proxy forces.
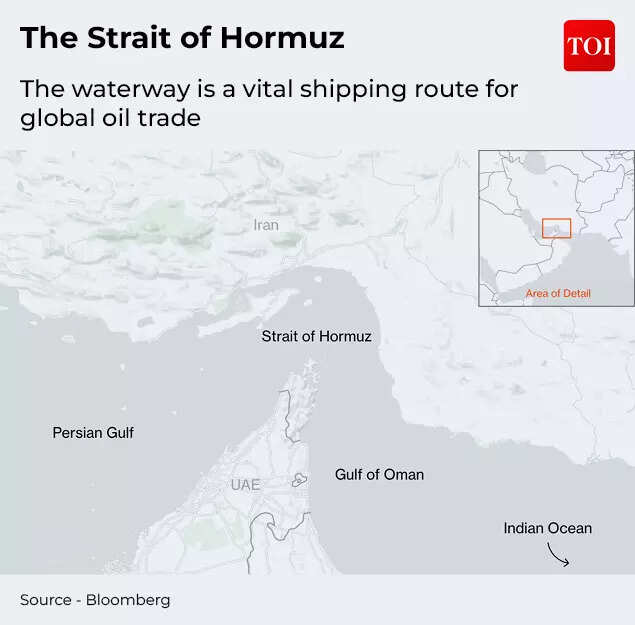
Strait of Hormuz
The most immediate economic impact is expected in energy markets, where crude oil and natural gas prices are likely to move higher, they say. Such actions, feel analysts, will keep geopolitical risk premiums at high levels. In 2024, approximately 20 million barrels per day moved through the Strait of Hormuz, which is around one-fifth of global petroleum liquids consumption. Even a limited interference – which can be caused by delays, rerouting, or isolated seizure – can push prices higher through increased risk perception well before any actual shortages emerge.Liquefied natural gas should not be overlooked in this context. Qatar has the world’s third-largest LNG export capacity, and roughly one-fifth of global LNG shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, largely consisting of Qatari exports. As a result, shipping risks in the region affect gas markets as significantly as oil markets.Also Read | US-Israel strikes on Iran: How will India be hit by Strait of Hormuz closure? ExplainedShipping expenses have already begun to rise, with insurance costs acting as a major driver. Insurers have started issuing cancellation notices and revising war-risk premiums for voyages in the Gulf region. Some routes have reportedly seen premium increases of up to about 50%, while earlier periods of tension recorded rises exceeding 60% on important trade corridors. These developments effectively tighten supply conditions even when production levels remain unchanged.The possibility of the conflict spreading across the region is increasing. Franklin Templeton Institute analysts are of the view that across global financial markets, the immediate response to such shocks is usually driven by adjustments in risk perception rather than by underlying economic changes. “The initial market reaction for this type of event would typically see Treasury yields move lower and equities lower—mostly a risk-premium repricing. Impacts on activity/earnings may be delayed and uneven. The US dollar reaction is not guaranteed; gold tends to benefit while bitcoin has been trading like a risk asset (i.e., down with equities), reinforcing that it’s not typically a reliable hedge/diversifier in geopolitical drawdowns,” say Franklin Templeton Institute analysts.However, they note that experience shows markets often come to view geopolitical disruptions as temporary. Initial spikes in risk premiums are frequently followed by the realization that the overall effect on corporate profitability is limited. The duration of the conflict, developments in shipping and insurance costs, and the eventual resolution will be more important than the initial headlines.“We would not yet label this a clean buy-the-dip setup—duration, shipping/insurance mechanics, and the endgame matter more than the first headline,” they say.From an investment perspective, the near-term outlook favours sectors linked to energy markets, as well as companies benefiting from higher shipping and insurance costs, along with defence-related industries, the analysts say. At the same time, caution is warranted toward emerging markets that depend heavily on energy imports and toward cyclical sectors sensitive to fuel and logistics costs, including airlines and certain industrial segments.“For protection, we prefer oil upside/volatility structures and selective gold exposure over broad equity shorts—the path will be driven more by shipping/insurance reality than by the new cycle,” they conclude.
Business
Oil jumps 10% and could spike to $100 a barrel, analysts warn

Brent crude jumped 10% to about $80 a barrel over the counter on Sunday, oil traders said, while analysts predicted that prices could climb as high as $100 after U.S. and Israeli strikes on Iran plunged the Middle East into a new war.
The primary driver of this market volatility is the critical Strait of Hormuz. Ajay Parmar, director of energy and refining at ICIS, stated: “While the military attacks are themselves supportive for oil prices, the key factor here is the closing of the Strait of Hormuz.”
Most tanker owners, oil majors and trading houses have suspended crude oil, fuel and liquefied natural gas shipments via the Strait of Hormuz, trade sources said, after Tehran warned ships against moving through the waterway. More than 20% of global oil is moved through the Strait of Hormuz.
“We expect prices to open (after the weekend) much closer to $100 a barrel and perhaps exceed that level if we see a prolonged outage of the Strait,” Parmar said.
Middle East leaders have warned Washington that a war on Iran could lead to oil prices jumping to more than $100 a barrel, said RBC analyst Helima Croft. Barclays analysts also said prices could hit $100.
The OPEC+ group of oil producers agreed on Sunday to raise output by 206,000 barrels per day (bpd) from April, a modest increase representing less than 0.2% of global demand.
While some alternate infrastructure could be used to bypass the Strait of Hormuz, the net impact from its closure would be a loss of 8 million to 10 million bpd of crude oil supply even after diverting some flows through Saudi Arabia’s East-West pipeline and Abu Dhabi pipeline, said Rystad energy economist Jorge Leon.
Rystad expects prices to rise by $20 to about $92 a barrel when trade opens.
The Iran crisis also prompted Asian governments and refiners to assess oil stockpiles and alternative shipping routes and supplies.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThese Cheap Noise-Cancelling Sony Headphones Are Even Cheaper Right Now
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThe Supreme Court’s Tariff Ruling Won’t Bring Car Prices Back to Earth
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoViral monkey Punch makes IKEA toy global sensation: Here’s what it costs
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoSaturday Sessions: Say She She performs "Under the Sun"
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEquinox chairman says ‘health is the new luxury’ as wellness spending soars












