Business
Best Buy hikes sales forecast as shoppers upgrade tech, splurge on devices

A Best Buy store in Pinole, California, US, on Monday, Nov. 24, 2025. Best Buy Co. is expected to release earnings figures on November 25.
David Paul Morris | Bloomberg | Getty Images
Best Buy hiked its full-year forecast Tuesday, as it topped Wall Street’s quarterly sales expectations and customers turned to the retailer to upgrade laptops and splurge on new gaming consoles and smartphones.
The consumer electronics retailer said it now expects revenue of between $41.65 billion to $41.95 billion for the full year, higher than its previous range of $41.1 billion to $41.9 billion. It expects adjusted earnings per share of $6.25 to $6.35, compared with its prior range of $6.15 to $6.30.
Best Buy said it expects full-year comparable sales, a metric that tracks sales online and at stores open at least 14 months, to range between a 0.5% rise to a 1.2% increase, compared with its previous expectations for a 1% decline and a 1% climb.
On the company’s earnings call, CEO Corie Barry said Best Buy saw “better-than-expected” sales in the quarter because of strong results across computing, gaming and mobile phones, as well as growth in wearables and headphones. She said sales rose across both its website and stores.
She said customer shopping behavior in the most recent three-month period was about the same as what Best Buy has seen for the past several quarters.
“Customers remain resilient, but deal focused and attracted to more predictable sales moments,” such as back-to-school sales and Best Buy’s October sale that coincided with Amazon’s Prime Day event, she said.
And she said, “while customers continued to be thoughtful about big ticket purchases in the current environment, they are willing to spend on high priced point products when they need to or when there is technology innovation.”
Here’s how the retailer did for the three-month period that ended Nov. 1 compared with what Wall Street was expecting, according to a survey of analysts by LSEG:
- Earnings per share: $1.40 adjusted vs. $1.31 expected
- Revenue: $9.67 billion vs. $9.59 billion expected
Shares were up about 6% in afternoon trading on Tuesday. As of Monday’s close, Best Buy’s stock has dropped by about 12% this year. That compares with the 14% gains of the S&P 500 during the same period.
Best Buy has been waiting for some of the key catalysts that tend to drive its business, such as higher housing turnover that leads to appliance purchases, the tech innovations that spark demand for devices and expert advice, and the increased willingness by inflation-weary consumers to splurge on discretionary items.
Some of that tech innovation appears to be gaining momentum with sales of the Nintendo Switch 2, new iPhones and AI-enabled laptops. The company called out those merchandise categories as strengths in the most recent three-month period.
Best Buy’s net income for the fiscal third quarter fell to $140 million, or 66 cents per share, from net income of $273 million, or $1.26 per share, in the year-ago period. Adjusting for one-time items, including stock-based compensation and restructuring charges, Best Buy reported earnings of $1.40.
Revenue rose from $9.45 billion in the year-ago quarter.
Best Buy’s comparable sales increased 2.7% year over year. That was the company’s highest comparable sales growth in four years, Barry said.
In the U.S., the metric jumped 2.4%, as shoppers bought computers, gaming systems and mobile phones, but purchased fewer appliances and home theaters.
Getting ready for the holidays
Best Buy’s annual revenue has dropped for the past three years. With the updated guidance, the company expects annual revenue to be slightly higher than last year’s total of $41.53 billion.
Still, like other retailers, Best Buy said it’s continuing to see shoppers spend selectively and seek out value, and anticipates that will carry into the holiday season, Barry said on a call with reporters.
“We absolutely are seeing people make trade offs,” she said.
For instance, she said, some customers are buying TVs in the middle or lower tier of its price range rather than premium TVs. However, she said Best Buy’s reputation as a specialty retailer with many different brands and price points is helping it attract more low-income and younger customers.
As the holiday season heats up, Barry said the company is ready for key sales days like Black Friday and Cyber Monday and will have “deals across the spectrum for whenever people want to shop.”
Even so, the retailer gave a cautious outlook for the holiday quarter, saying it expects sales trends to decelerate from the previous quarter. Bilunas said the company expects comparable sales during the period to range from a 1% decline to a 1% increase.
On the company’s earnings call, he said Best Buy is seeing “positive growth” in the fourth quarter and a roughly similar trend to the third quarter, but faces tougher year over year comparisons and may see waning trends in some categories like gaming and wearables. In gaming, Nintendo Switch 2 sales haven’t been as strong as they were closer to the June launch.
“Obviously, the holiday is never easy to predict,” he said.” What we do believe is that we have a range of scenarios and the range we’ve provided gives us a great place to plan and plan our business operationally.”
Higher tariffs will be a complicating factor for the rest of the year, both in how they affect the company’s costs and consumer spending. On the company’s earnings call, Bilunas said higher tariffs so far haven’t had a meaningful impact on Best Buy’s prices or its sales. He said growth is coming from more unit sales.
Compared to other industries, he said, consumer electronics are a very promotional category and that’s muted the impact on average selling prices, he said.
Trying out Meta glasses, Sharkninja appliances
At Best Buy’s stores, the company has tried to give customers more reasons to try products by adding more vendor demos, Barry said on the company’s earnings call. For example, she said more than 50 of its locations have immersive showcase areas for Meta’s latest AI-enabled glasses, and demand for in-person demos has outpaced available appointments.
It has launched most of its pilot showrooms with Ikea, which it is testing in 10 stores across Texas and Florida. And other vendors, including Breville and Sharkninja, are also showing off items for home baristas and chefs or customers looking for health and beauty devices in its stores, she said.
Barry said “very early reads are positive and we are excited to monitor customer response during the holidays.”
To help drive growth, Best Buy also launched a third-party marketplace in mid-August to expand the brands and the items that it sells. About three months into the launch, the company has more than 1,000 sellers and 11 times more individual items available for online customers than it did before, Barry said on the earnings call.
So far, she said the company is seeing higher sales in categories like accessories and small appliances. She said customer return rates for marketplace items have run lower than first-party purchases, and more than 80% of marketplace product returns by customers have been at stores.
As the marketplace grows, she said it’s driving higher profits and creating new opportunities for Best Buy to sell online ads.
Despite the positive signs, some of Best Buy’s categories, including appliances, continue to lag.
Chief Financial Officer Matt Bilunas said the appliance category is “probably the most difficult one that we have in the market today.” He said historically, the company has sold new premium appliances and sets of appliances.
With the slower housing market, he said the company is seeing more shoppers replace a product that’s broken rather than buy a washer and dryer pair, and promotions haven’t been as effective. To speed up sales, Best Buy plans to increase its labor in the department, speed up deliveries to better compete with rivals and even make some items available same day, he said.
“And hopefully as housing and different things change, then the market starts to swing back to something that might be a little bit more normal,” he said.
Business
Flights cancelled as new travel warnings issued after US-Israeli strikes on Iran

BA and Virgin Atlantic are among major airlines to ground services to the Middle East in light of the attacks.
Source link
Business
Two ships hit near Strait of Hormuz as fears grow of oil price rises
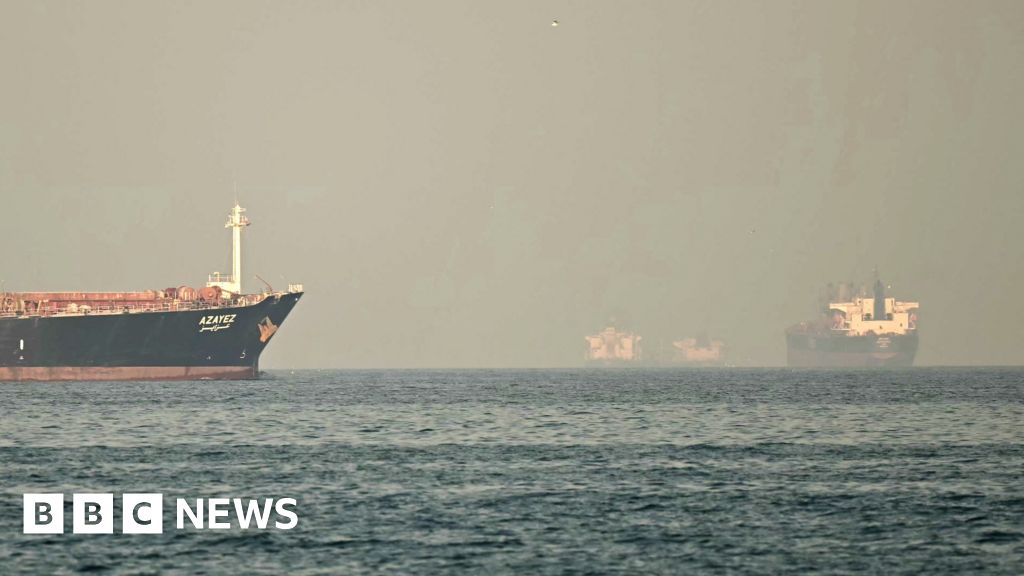

International shipping is said to have come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with fears of disruption already pushing up global oil prices.
Source link
Business
Khamenei dead, Middle East on edge: What will be the implications of Trump’s ‘Epic fury’ on stock markets, gold & oil? – The Times of India

The global markets are in for a phase of enhanced turmoil and uncertainty! The ongoing tensions in the Middle East after US and Israel’s strikes on Iran and Ali Khamenei’s death may have investors running for cover – looking for an asset class that is safer.During the night of February 27–28, the United States and Israel carried out joint aerial strikes on Iran as part of “Operation Epic Fury.” Statements by President Trump openly referring to regime change suggest that the confrontation could evolve into a prolonged campaign rather than remain a limited exchange, say market analysts at Franklin Templeton Institute.What does the situation mean for stock markets, energy markets (oil), gold and other asset classes? Here’s what Franklin Templeton Institute analysts have to say:From a market perspective, the key uncertainty is whether the conflict remains confined to direct military engagement or expands into disruptions affecting energy supplies and logistics networks, which would sustain a higher and more persistent risk premium.At the centre of the ongoing uncertainty from a global market and trade perspective is the Strait of Hormuz. While a complete blockade would carry severe consequences for Iran itself, the country has the capability to disrupt maritime traffic through tactics such as vessel harassment, seizures, drone activity, cyber operations, or the use of proxy forces.
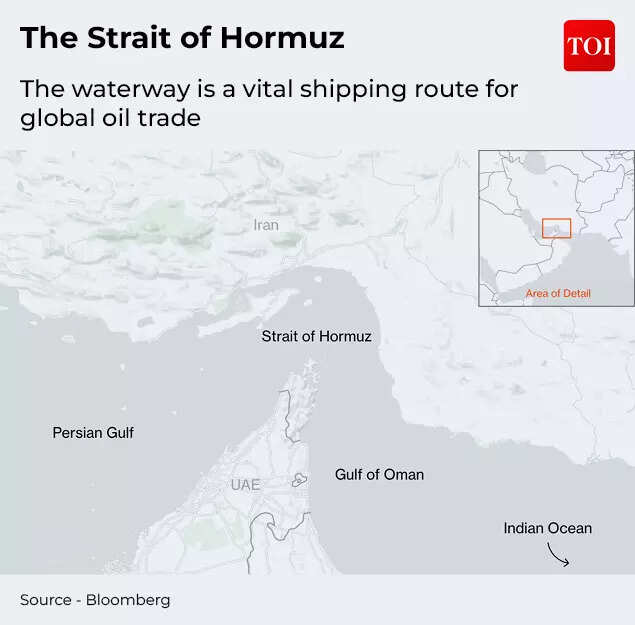
Strait of Hormuz
The most immediate economic impact is expected in energy markets, where crude oil and natural gas prices are likely to move higher, they say. Such actions, feel analysts, will keep geopolitical risk premiums at high levels. In 2024, approximately 20 million barrels per day moved through the Strait of Hormuz, which is around one-fifth of global petroleum liquids consumption. Even a limited interference – which can be caused by delays, rerouting, or isolated seizure – can push prices higher through increased risk perception well before any actual shortages emerge.Liquefied natural gas should not be overlooked in this context. Qatar has the world’s third-largest LNG export capacity, and roughly one-fifth of global LNG shipments pass through the Strait of Hormuz, largely consisting of Qatari exports. As a result, shipping risks in the region affect gas markets as significantly as oil markets.Also Read | US-Israel strikes on Iran: How will India be hit by Strait of Hormuz closure? ExplainedShipping expenses have already begun to rise, with insurance costs acting as a major driver. Insurers have started issuing cancellation notices and revising war-risk premiums for voyages in the Gulf region. Some routes have reportedly seen premium increases of up to about 50%, while earlier periods of tension recorded rises exceeding 60% on important trade corridors. These developments effectively tighten supply conditions even when production levels remain unchanged.The possibility of the conflict spreading across the region is increasing. Franklin Templeton Institute analysts are of the view that across global financial markets, the immediate response to such shocks is usually driven by adjustments in risk perception rather than by underlying economic changes. “The initial market reaction for this type of event would typically see Treasury yields move lower and equities lower—mostly a risk-premium repricing. Impacts on activity/earnings may be delayed and uneven. The US dollar reaction is not guaranteed; gold tends to benefit while bitcoin has been trading like a risk asset (i.e., down with equities), reinforcing that it’s not typically a reliable hedge/diversifier in geopolitical drawdowns,” say Franklin Templeton Institute analysts.However, they note that experience shows markets often come to view geopolitical disruptions as temporary. Initial spikes in risk premiums are frequently followed by the realization that the overall effect on corporate profitability is limited. The duration of the conflict, developments in shipping and insurance costs, and the eventual resolution will be more important than the initial headlines.“We would not yet label this a clean buy-the-dip setup—duration, shipping/insurance mechanics, and the endgame matter more than the first headline,” they say.From an investment perspective, the near-term outlook favours sectors linked to energy markets, as well as companies benefiting from higher shipping and insurance costs, along with defence-related industries, the analysts say. At the same time, caution is warranted toward emerging markets that depend heavily on energy imports and toward cyclical sectors sensitive to fuel and logistics costs, including airlines and certain industrial segments.“For protection, we prefer oil upside/volatility structures and selective gold exposure over broad equity shorts—the path will be driven more by shipping/insurance reality than by the new cycle,” they conclude.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPakistan carries out precision strikes on seven militant hideouts in Afghanistan
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEye-popping rise in one year: Betting on just gold and silver for long-term wealth creation? Think again! – The Times of India
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoKansas’ Darryn Peterson misses most of 2nd half with cramping
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThe Supreme Court’s Tariff Ruling Won’t Bring Car Prices Back to Earth
-

 Tech1 week ago
Tech1 week agoThese Cheap Noise-Cancelling Sony Headphones Are Even Cheaper Right Now
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoEquinox chairman says ‘health is the new luxury’ as wellness spending soars
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoViral monkey Punch makes IKEA toy global sensation: Here’s what it costs
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoSaturday Sessions: Say She She performs "Under the Sun"












